Difference between revisions of "Vaishya"
(Created page with "thumb|250px| '''Vaishya''' is one of the four varnas of the Hindu social order. Duties of Vaishyas According to the Hindu texts, the duties of a Vai...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Casteimage1.JPG|thumb|250px|]] | [[File:Casteimage1.JPG|thumb|250px|]] | ||
| − | '''Vaishya''' is one of the four varnas of the Hindu social order. | + | '''[[Vaishya]]''' is one of the four varnas of the [[Hindu]] {{Wiki|social}} [[order]]. |
| − | Duties of Vaishyas | + | Duties of [[Vaishyas]] |
| − | According to the Hindu texts, the duties of a Vaishyas included cattle rearing and other pastoral tasks, productive labor, agriculture and trade. The Vaisyas, along with the Brahmins and Kshatriyas, claim to be of the "twice born" (dvija) castes of the classical theory. Indian traders were widely credited for the spread of Indian culture to regions as far as southeast Asia. | + | According to the {{Wiki|Hindu texts}}, the duties of a [[Vaishyas]] included cattle rearing and other pastoral tasks, productive labor, {{Wiki|agriculture}} and trade. The [[Vaisyas]], along with the [[Brahmins]] and {{Wiki|Kshatriyas}}, claim to be of the "twice born" (dvija) castes of the classical {{Wiki|theory}}. [[Indian]] traders were widely credited for the spread of [[Indian]] {{Wiki|culture}} to regions as far as {{Wiki|southeast}} {{Wiki|Asia}}. |
| − | Historically, Vaisyas have played a much larger role in Indian affairs apart from trade and commerce. According to Ram Sharan Sharma, a historian, the Gupta Empire was a Vaishya dynasty that "may have appeared as a reaction against oppressive rulers". A.S. Altekar, a historian and archaeologist, who has written several books on Gupta coinage, also regarded the caste of the Guptas as Vaishya on the basis of the ancient Indian texts on law, which prescribe the name-ending with Gupta for a member of the Vaishya caste. | + | Historically, [[Vaisyas]] have played a much larger role in [[Indian]] affairs apart from trade and commerce. According to Ram Sharan Sharma, a historian, the Gupta [[Empire]] was a [[Vaishya]] dynasty that "may have appeared as a {{Wiki|reaction}} against oppressive rulers". A.S. Altekar, a historian and archaeologist, who has written several [[books]] on Gupta coinage, also regarded the [[caste]] of the Guptas as [[Vaishya]] on the basis of the {{Wiki|ancient Indian}} texts on law, which prescribe the name-ending with Gupta for a member of the [[Vaishya]] [[caste]]. |
| − | Modern communities | + | {{Wiki|Modern}} communities |
| − | The Vaisya community consist of several jāti or subcaste, notably the Agrawals, the Barnwals,the Roniaurs or the Rouniyars by Er. Sumit Sagar ],the Gahois, the Kasuadhans, the Patwa, the Khandelwals, the Oswals, Rastogis, Lohanas and the Maheshwaris of the north; the Arya Vaishyas of Andhra pradesh, Vanika Vaishyas of the Kerala, Cenkuntar of Tamil Nadu, the Vaishya Vanis of Konkan and Goa, Ladshakhiy Wani in North and Western Maharashtra and the Modh, Beesa Neema, Dasa Neema, Dasore, Parekhs and Patidars of the west. | + | The Vaisya community consist of several [[jāti]] or subcaste, notably the Agrawals, the Barnwals,the Roniaurs or the Rouniyars by Er. Sumit Sagar ],the Gahois, the Kasuadhans, the Patwa, the Khandelwals, the Oswals, Rastogis, Lohanas and the Maheshwaris of the {{Wiki|north}}; the [[Arya]] [[Vaishyas]] of Andhra pradesh, Vanika [[Vaishyas]] of the {{Wiki|Kerala}}, Cenkuntar of Tamil Nadu, the [[Vaishya]] Vanis of Konkan and Goa, Ladshakhiy Wani in {{Wiki|North}} and Western [[Maharashtra]] and the Modh, Beesa Neema, Dasa Neema, Dasore, Parekhs and Patidars of the {{Wiki|west}}. |
{{W}} | {{W}} | ||
[[Category:Buddhist Terms]] | [[Category:Buddhist Terms]] | ||
[[Category:Sanskrit terminology]] | [[Category:Sanskrit terminology]] | ||
[[Category:India]] | [[Category:India]] | ||
Revision as of 21:19, 19 September 2013
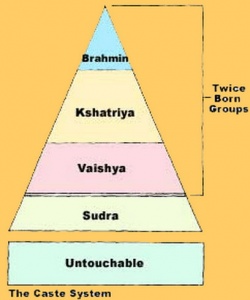
Vaishya is one of the four varnas of the Hindu social order.
Duties of Vaishyas
According to the Hindu texts, the duties of a Vaishyas included cattle rearing and other pastoral tasks, productive labor, agriculture and trade. The Vaisyas, along with the Brahmins and Kshatriyas, claim to be of the "twice born" (dvija) castes of the classical theory. Indian traders were widely credited for the spread of Indian culture to regions as far as southeast Asia.
Historically, Vaisyas have played a much larger role in Indian affairs apart from trade and commerce. According to Ram Sharan Sharma, a historian, the Gupta Empire was a Vaishya dynasty that "may have appeared as a reaction against oppressive rulers". A.S. Altekar, a historian and archaeologist, who has written several books on Gupta coinage, also regarded the caste of the Guptas as Vaishya on the basis of the ancient Indian texts on law, which prescribe the name-ending with Gupta for a member of the Vaishya caste. Modern communities
The Vaisya community consist of several jāti or subcaste, notably the Agrawals, the Barnwals,the Roniaurs or the Rouniyars by Er. Sumit Sagar ],the Gahois, the Kasuadhans, the Patwa, the Khandelwals, the Oswals, Rastogis, Lohanas and the Maheshwaris of the north; the Arya Vaishyas of Andhra pradesh, Vanika Vaishyas of the Kerala, Cenkuntar of Tamil Nadu, the Vaishya Vanis of Konkan and Goa, Ladshakhiy Wani in North and Western Maharashtra and the Modh, Beesa Neema, Dasa Neema, Dasore, Parekhs and Patidars of the west.