Difference between revisions of "Conch Shell in Buddhism"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Ashtamangala_right_whorl_conch.png|thumb|250px|]] | [[File:Ashtamangala_right_whorl_conch.png|thumb|250px|]] | ||
{{Seealso|Conch}} | {{Seealso|Conch}} | ||
| − | The [[conch shell]] (Sanskrit [[shankha]]; Tibetan [[dung dkar]]) has survived as the original horn {{Wiki|trumpet}} since time immemorial. Ancient Indian {{Wiki|epics}} describe how each hero of {{Wiki|mythical}} warfare carried a mighty white [[conch shell]], which often bore a personal name. | + | The [[conch shell]] ([[Sanskrit]] [[shankha]]; [[Tibetan]] [[dung dkar]]) has survived as the original horn {{Wiki|trumpet}} since time immemorial. {{Wiki|Ancient Indian}} {{Wiki|epics}} describe how each [[hero]] of {{Wiki|mythical}} warfare carried a mighty white [[conch shell]], which often bore a personal [[name]]. |
| − | It is one of the main {{Wiki|emblems}} of {{Wiki|Vishnu}}, and his [[conch]] bears the name of [[Panchajanya]], meaning 'having control over the five classes of beings.' | + | It is one of the main {{Wiki|emblems}} of {{Wiki|Vishnu}}, and his [[conch]] bears the [[name]] of [[Panchajanya]], meaning 'having control over the five classes of [[beings]].' |
| − | {{Wiki|Arjuna}}'s (hero of the {{Wiki|Mahabharata}}) mighty conch was known as {{Wiki|Devadatta}}, whose {{Wiki|triumphant}} blast brought {{Wiki|terror}} to the {{Wiki|enemy}}. As a proclaiming {{Wiki|battle}} {{Wiki|horn}}, the [[conch]] is akin to the bugle. It is an {{Wiki|emblem}} of power, authority and sovereignty whose blast is believed to banish [[evil]] [[spirits]], avert natural disasters, and scare away poisonous creatures. | + | {{Wiki|Arjuna}}'s ([[hero]] of the {{Wiki|Mahabharata}}) mighty [[conch]] was known as {{Wiki|Devadatta}}, whose {{Wiki|triumphant}} blast brought {{Wiki|terror}} to the {{Wiki|enemy}}. As a proclaiming {{Wiki|battle}} {{Wiki|horn}}, the [[conch]] is akin to the bugle. It is an {{Wiki|emblem}} of power, authority and {{Wiki|sovereignty}} whose blast is believed to banish [[evil]] [[spirits]], avert natural {{Wiki|disasters}}, and scare away {{Wiki|poisonous}} creatures. |
| − | Today, in its greatly tamed {{Wiki|avatar}}, the [[conch]] is used in [[Tibetan Buddhism]] to call together [[religious]] {{Wiki|assemblies}}. During the actual practise of [[rituals]], it is used both as a musical instrument and as a container for holy water. | + | Today, in its greatly tamed {{Wiki|avatar}}, the [[conch]] is used in [[Tibetan Buddhism]] to call together [[religious]] {{Wiki|assemblies}}. During the actual practise of [[rituals]], it is used both as a musical instrument and as a container for {{Wiki|holy}} [[water]]. |
| − | Ancient {{Wiki|Indian}} [[belief]] classifies the [[conch]] into {{Wiki|male}} and {{Wiki|female}} varieties. The thicker-shelled bulbous one is thought to be the {{Wiki|male}} ({{Wiki|purusha}}), and the thin-shelled slender conch to be the {{Wiki|female}} ({{Wiki|shankhini}}). | + | [[Ancient]] {{Wiki|Indian}} [[belief]] classifies the [[conch]] into {{Wiki|male}} and {{Wiki|female}} varieties. The thicker-shelled bulbous one is [[thought]] to be the {{Wiki|male}} ({{Wiki|purusha}}), and the thin-shelled slender [[conch]] to be the {{Wiki|female}} ({{Wiki|shankhini}}). |
| − | The fourfold caste division is also applied as follows: | + | The fourfold [[caste]] [[division]] is also applied as follows: |
| − | * The smooth white [[conch]] represents the {{Wiki|Brahmin}} caste ({{Wiki|priests}}) | + | * The smooth white [[conch]] represents the {{Wiki|Brahmin}} [[caste]] ({{Wiki|priests}}) |
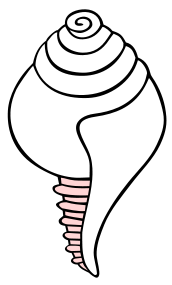
| − | * The red conch, the {{Wiki|kshatriyas}} ({{Wiki|warriors}}) | + | * The [[red]] [[conch]], the {{Wiki|kshatriyas}} ({{Wiki|warriors}}) |
| − | * The yellow conch, the {{Wiki|vaishyas}} ({{Wiki|merchants}}) | + | * The [[yellow]] [[conch]], the {{Wiki|vaishyas}} ({{Wiki|merchants}}) |
| − | * The grey conch, the {{Wiki|shudras}} ({{Wiki|labourers}}) | + | * The grey [[conch]], the {{Wiki|shudras}} ({{Wiki|labourers}}) |
| − | Additionally, there is a fundamental classification of [[conch shells]] occurring in nature: those that turn to the left and those which turn to the right. Shells which spiral to the right in a clockwise direction are a rarity and are considered especially {{Wiki|sacred}}. The right-spiralling movement of such a [[conch]] is believed to echo the {{Wiki|celestial}} motion of the {{Wiki|sun}}, {{Wiki|moon}}, {{Wiki|planets}} and {{Wiki|stars}} across the [[heavens]]. The hair whorls on [[Buddha]]'s head spiral to the right, as do his fine [[body]] hairs, the long curl between his eyebrows ([[urna]]), and also the [[conch]]-like swirl of his navel. | + | Additionally, there is a fundamental {{Wiki|classification}} of [[conch shells]] occurring in [[nature]]: those that turn to the left and those which turn to the right. Shells which spiral to the right in a {{Wiki|clockwise}} [[direction]] are a rarity and are considered especially {{Wiki|sacred}}. The right-spiralling {{Wiki|movement}} of such a [[conch]] is believed to {{Wiki|echo}} the {{Wiki|celestial}} {{Wiki|motion}} of the {{Wiki|sun}}, {{Wiki|moon}}, {{Wiki|planets}} and {{Wiki|stars}} across the [[heavens]]. The [[hair]] whorls on [[Buddha]]'s head spiral to the right, as do his fine [[body]] hairs, the long curl between his [[eyebrows]] ([[urna]]), and also the [[conch]]-like swirl of his {{Wiki|navel}}. |
| − | [[Vajrayana Buddhism]] absorbed the [[conch]] as a [[symbol]] which fearlessly proclaimed the [[truth]] of the [[dharma]]. Among the [[eight symbols]], it stands for the [[fame]] of the [[Buddha]]'s teaching, which spreads in all directions like the sound of the [[conch]] {{Wiki|trumpet}}. | + | [[Vajrayana Buddhism]] absorbed the [[conch]] as a [[symbol]] which fearlessly proclaimed the [[truth]] of the [[dharma]]. Among the [[eight symbols]], it stands for the [[fame]] of the [[Buddha]]'s [[teaching]], which spreads in all [[directions]] like the [[sound]] of the [[conch]] {{Wiki|trumpet}}. |
| − | In addition to [[Buddha]]'s throat, the [[conch]] also appears as an {{Wiki|auspicious}} mark on the soles, {{Wiki|palms}}, {{Wiki|limbs}}, {{Wiki|breast}} or {{Wiki|forehead}} of a {{Wiki|divinely}} endowed being. | + | In addition to [[Buddha]]'s {{Wiki|throat}}, the [[conch]] also appears as an {{Wiki|auspicious}} mark on the soles, {{Wiki|palms}}, {{Wiki|limbs}}, {{Wiki|breast}} or {{Wiki|forehead}} of a {{Wiki|divinely}} endowed being. |
{{R}} | {{R}} | ||
[http://www.religionfacts.com/buddhism/symbols/conch.htm religionfacts.com] | [http://www.religionfacts.com/buddhism/symbols/conch.htm religionfacts.com] | ||
[[Category:Conch]] | [[Category:Conch]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:39, 6 January 2024
- See also :
- See also :
The conch shell (Sanskrit shankha; Tibetan dung dkar) has survived as the original horn trumpet since time immemorial. Ancient Indian epics describe how each hero of mythical warfare carried a mighty white conch shell, which often bore a personal name.
It is one of the main emblems of Vishnu, and his conch bears the name of Panchajanya, meaning 'having control over the five classes of beings.'
Arjuna's (hero of the Mahabharata) mighty conch was known as Devadatta, whose triumphant blast brought terror to the enemy. As a proclaiming battle horn, the conch is akin to the bugle. It is an emblem of power, authority and sovereignty whose blast is believed to banish evil spirits, avert natural disasters, and scare away poisonous creatures.
Today, in its greatly tamed avatar, the conch is used in Tibetan Buddhism to call together religious assemblies. During the actual practise of rituals, it is used both as a musical instrument and as a container for holy water.
Ancient Indian belief classifies the conch into male and female varieties. The thicker-shelled bulbous one is thought to be the male (purusha), and the thin-shelled slender conch to be the female (shankhini).
The fourfold caste division is also applied as follows:
- The smooth white conch represents the Brahmin caste (priests)
- The red conch, the kshatriyas (warriors)
- The yellow conch, the vaishyas (merchants)
- The grey conch, the shudras (labourers)
Additionally, there is a fundamental classification of conch shells occurring in nature: those that turn to the left and those which turn to the right. Shells which spiral to the right in a clockwise direction are a rarity and are considered especially sacred. The right-spiralling movement of such a conch is believed to echo the celestial motion of the sun, moon, planets and stars across the heavens. The hair whorls on Buddha's head spiral to the right, as do his fine body hairs, the long curl between his eyebrows (urna), and also the conch-like swirl of his navel.
Vajrayana Buddhism absorbed the conch as a symbol which fearlessly proclaimed the truth of the dharma. Among the eight symbols, it stands for the fame of the Buddha's teaching, which spreads in all directions like the sound of the conch trumpet.
In addition to Buddha's throat, the conch also appears as an auspicious mark on the soles, palms, limbs, breast or forehead of a divinely endowed being.