Difference between revisions of "Buddhist Symbols, The Becon Lights to Nibbana by Ven. Dr.Bhikkhu Bodhipala"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DisplayImages|2959}} | {{DisplayImages|2959}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{Centre|<big><big>Buddhist Symbols, The Becon Lights To Nibbana</big></big><br/> | {{Centre|<big><big>Buddhist Symbols, The Becon Lights To Nibbana</big></big><br/> | ||
By<br/> | By<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Ven. Dr.Bhikkhu Bodhipala<br/> | Ven. Dr.Bhikkhu Bodhipala<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
M.A., M.A., M.Phil., D.I.R.D., D.G.Th., Ph.D.,(B.G.L)<br/> | M.A., M.A., M.Phil., D.I.R.D., D.G.Th., Ph.D.,(B.G.L)<br/> | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[[Symbols]]=== | ===[[Symbols]]=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Symbols]] at any rate are the most deep rooted [[elements]] of [[human]] [[consciousness]]. They may be developed into highly {{Wiki|aesthetic}} [[forms]] yet their efficacy never depends on their {{Wiki|aesthetic}} values. The [[success]] of [[religions]] of the [[world]] is due to [[development]] of [[symbols]] within the particular [[religion]] itself out of [[spiritual]] gain or [[experience]] of its followers. A wooden [[wheel]] just having eight spokes is nothing but a [[representation]] of entire [[teachings of the Buddha]]. Likewise just two wooden poles put crosswise is the [[symbol]] of entire [[Christianity]]. A small doll is also a [[symbol]] which gives several meanings to a playing child. So [[symbols]] are sign of [[development]] of [[human]] [[consciousness]], in the field of [[art]], {{Wiki|literature}} eventually end in [[spiritual experience]]. | + | |
| + | The [[Forms]], figures, drawings, even animal’s heads, marks, {{Wiki|color}} lights, all materials what the humankind uses in his day to day [[life]] act as [[symbols]] to give a different meaning and conveing a message to the ‘onlookers’ in a particular context and in a particular place. For example a [[symbol]] depicting a [[skull]] put on two thigh {{Wiki|bones}} warns the seers ‘It is a [[danger]] thing | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | and eventually may leading to [[death]]’. An ‘X’ made up of spoon and fork and displayed on the road side indicates the presence of a ‘motel’ or a place of ‘refreshment’.Like this we can give [[endless]] examples. Shortly {{Wiki|speaking}} a [[symbol]] gives a message it may be a request or a warning or an order and even a [[spiritual]] intimation. Letters and numbers also be [[symbols]], because the [[evolution]] of | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[symbols]] would be a transition from an ideographic to a phonetic scripts which may be or a progress from the {{Wiki|linguistic}} stand point or from the {{Wiki|practical}} use. In [[ancient]] {{Wiki|Egypt}} even figures of [[animals]], birds and {{Wiki|reptiles}} stood for | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | letters. In [[Chinese language]] just lines either vertical or horizontal or crosswise or a triangle all stand for conveying the [[ideas]] rather than the letters and [[language]]. Shortly {{Wiki|speaking}} a [[form]] or a figure which stands for an [[idea]] becomes a [[symbol]] as such a [[symbol]] is not mere a [[form]] or a picture but {{Wiki|perfect}} [[manifestation]] or expression of [[experience]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Symbols]] at any rate are the most deep rooted [[elements]] of [[human]] [[consciousness]]. They may be developed into highly {{Wiki|aesthetic}} [[forms]] yet their efficacy never depends on their {{Wiki|aesthetic}} values. The [[success]] of [[religions]] of the | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[world]] is due to [[development]] of [[symbols]] within the particular [[religion]] itself out of [[spiritual]] gain or [[experience]] of its followers. A wooden [[wheel]] just having eight spokes is nothing but a [[representation]] of entire [[teachings of the Buddha]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Likewise just two wooden poles put crosswise is the [[symbol]] of entire [[Christianity]]. A small doll is also a [[symbol]] which gives several meanings to a playing child. So [[symbols]] are sign of [[development]] of [[human]] [[consciousness]], in the field of [[art]], {{Wiki|literature}} eventually end in [[spiritual experience]]. | ||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
|[[File:Dhammachakka02015.jpg|thumb|250px|Symbol for [[eight-fold path]] ]] || [[File:56d64df5g4d.jpg|thumb|250px|Symbol for Christianity]] | |[[File:Dhammachakka02015.jpg|thumb|250px|Symbol for [[eight-fold path]] ]] || [[File:56d64df5g4d.jpg|thumb|250px|Symbol for Christianity]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===Type Of [[Symbols]]=== | ===Type Of [[Symbols]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
There are various types of [[symbols]] in current usages; THE PATTERN OF SYMBOLS varies according to needs and various fields and [[disciplines]]. Like [[science]] and technology for example lay out and circuits (in electronic field) do the works of the [[symbols]] and in History for example just putting B.C or AD or CE along with numbers gives more [[information]] to reckon the years in the field of history. | There are various types of [[symbols]] in current usages; THE PATTERN OF SYMBOLS varies according to needs and various fields and [[disciplines]]. Like [[science]] and technology for example lay out and circuits (in electronic field) do the works of the [[symbols]] and in History for example just putting B.C or AD or CE along with numbers gives more [[information]] to reckon the years in the field of history. | ||
| − | Chemical [[Science]]: In periodic table {{Wiki|Roman}} capital and small letters are marked to denote a type of metal or [[name]] of the metal or an [[element]]. ‘Au’ stands for {{Wiki|gold}}, likewise ‘Hg’, ‘O’, ‘N’, ‘Nd’, | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Chemical [[Science]]: In periodic table {{Wiki|Roman}} capital and small letters are marked to denote a type of metal or [[name]] of the metal or an [[element]]. ‘Au’ stands for {{Wiki|gold}}, likewise ‘Hg’, ‘O’, ‘N’, ‘Nd’, ‘’[[Na]]’, ‘H’, ‘Al’, ‘Cl’, and ‘Mg’, all these stand for {{Wiki|Mercury}}, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sodium, Hydrogen, Aluminum, Chlorine and Magnesium respectively. | ||
===Letters [[Standing]] For Numbers:=== | ===Letters [[Standing]] For Numbers:=== | ||
| − | In many [[languages]] of the [[world]], the ‘scripts or letters’ of the particular [[language]] are used as numbers. Capital {{Wiki|Roman}} letters are used as numbers, for example capital ‘I’ stands for number one likewise ‘I’ ‘II’ ‘III’ this sequential values1, 2, and 3 and capital ‘V’ stands for five, if capital ‘I’ is put on the left before capital ‘V’ value ‘one’ is deducted thus it will be the value of 4. If the capital ‘I’ is put ON THE RIGHT SIDE i.e after ‘V’ the value of 5 is increased, thus ‘V’,’VI’, ‘VII’, ‘VIII’ this sequential makes 5, 6, 7 and 8. Likewise the capital ‘X’ stands for value 10, if as above given method and if capital ‘I’ is put on left side the value ‘one’ is deducted as such it will be the value of 9. And when the capital ‘I’ is put on right side like ‘XI’, ‘XII’, ‘XIII’, the value is increasing as 11, 12 and 13. The capital ‘L’ stands for the value 40, if capital ‘X’ is put on the right side of capital ‘L’ the value would increase to 50. Shortly {{Wiki|speaking}} in {{Wiki|Latin}} [[language]] letters stand for numbers. On the same way the numbers in {{Wiki|Tamil}} [[Language]] are only its letters not separate [[symbols]] or numbers used. For example the first {{Wiki|vowel}} ‘A’ (Pronounced as ‘and’) stands for number 8 or value ‘eight’. The first consonant in {{Wiki|Tamil}} ‘Ka’ (pronounced as ‘cut’) stands for the value of ‘one’. Suppose ‘Ka’ and ‘A’ written left right it will be the value of 18 i.e eighteen and the same way ‘A’ and ‘Ka” put left right, it will be the value of 81 i.e eighty one. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | In many [[languages]] of the [[world]], the ‘scripts or letters’ of the particular [[language]] are used as numbers. Capital {{Wiki|Roman}} letters are used as numbers, for example capital ‘I’ stands for number one likewise ‘I’ ‘II’ ‘III’ this sequential values1, 2, and 3 and capital ‘V’ stands for five, if capital ‘I’ is put on the left before capital ‘V’ value ‘one’ is deducted thus it will be the value of 4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the capital ‘I’ is put ON THE RIGHT SIDE i.e after ‘V’ the value of 5 is increased, thus ‘V’,’VI’, ‘VII’, ‘VIII’ this sequential makes 5, 6, 7 and 8. Likewise the capital ‘X’ stands for value 10, if as above given method and if capital ‘I’ is put on left side the value ‘one’ is deducted as such it will be the value of 9. And when the capital ‘I’ is put on right side like ‘XI’, ‘XII’, ‘XIII’, the value is increasing | ||
| + | |||
| + | as 11, 12 and 13. The capital ‘L’ stands for the value 40, if capital ‘X’ is put on the right side of capital ‘L’ the value would increase to 50. Shortly {{Wiki|speaking}} in {{Wiki|Latin}} [[language]] letters stand for numbers. On the same way the numbers in {{Wiki|Tamil}} [[Language]] are only its letters not separate [[symbols]] or numbers used. For example the first {{Wiki|vowel}} ‘A’ (Pronounced as ‘and’) | ||
| + | |||
| + | stands for number 8 or value ‘eight’. The first consonant in {{Wiki|Tamil}} ‘Ka’ (pronounced as ‘cut’) stands for the value of ‘one’. Suppose ‘Ka’ and ‘A’ written left right it will be the value of 18 i.e eighteen and the same way ‘A’ and ‘Ka” put left right, it will be the value of 81 i.e eighty one. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[[Symbols]] In {{Wiki|Mathematics}}=== | ===[[Symbols]] In {{Wiki|Mathematics}}=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
When a child begins to do sums and calculations knowingly or unknowingly uses many [[symbols]] starting from ‘brackets’ ( ) ,‘(+)’ ,‘(-)’, ‘(X)’, ‘(%)’ ,’(<)’, ‘(>)’, ‘(|)’, ‘(\)’, ‘(/)’, ‘(=)’, and so on. | When a child begins to do sums and calculations knowingly or unknowingly uses many [[symbols]] starting from ‘brackets’ ( ) ,‘(+)’ ,‘(-)’, ‘(X)’, ‘(%)’ ,’(<)’, ‘(>)’, ‘(|)’, ‘(\)’, ‘(/)’, ‘(=)’, and so on. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[[Symbols]] In Litterary Works=== | ===[[Symbols]] In Litterary Works=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
In {{Wiki|Literary}} pieces also the role [[symbols]] are inevitable: ‘(,)’, ‘(.)’, ‘(;)’, ‘(:)’, ‘(?)’, ‘(!)’, and they express {{Wiki|poetic}} values and [[emotions]]. | In {{Wiki|Literary}} pieces also the role [[symbols]] are inevitable: ‘(,)’, ‘(.)’, ‘(;)’, ‘(:)’, ‘(?)’, ‘(!)’, and they express {{Wiki|poetic}} values and [[emotions]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===[[Symbols]] In The Hospitals=== | ===[[Symbols]] In The Hospitals=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
In all the hospitals, once we enter into it we come across many sign boards, figures which help everybody to reach or to get one’s requirement. | In all the hospitals, once we enter into it we come across many sign boards, figures which help everybody to reach or to get one’s requirement. | ||
As explained above [[symbols]]’ role is inevitable in all the fields of [[science]]. Right from road to home. | As explained above [[symbols]]’ role is inevitable in all the fields of [[science]]. Right from road to home. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==[[Buddhist]] [[Symbol]]== | ==[[Buddhist]] [[Symbol]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The [[Buddhist symbols]] are not concerned with [[mundane]] {{Wiki|purpose}} but they aim at [[spiritual]] goals and {{Wiki|purpose}}. | The [[Buddhist symbols]] are not concerned with [[mundane]] {{Wiki|purpose}} but they aim at [[spiritual]] goals and {{Wiki|purpose}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
A Good driver, if he follows all the road marks, sign boards, [[symbols]], [[directions]], signal lights he will be reaching his destination very safely in time. Likewise The [[Buddhist symbols]] are road [[signs]] to reach the abode of [[Enlightenment]]. | A Good driver, if he follows all the road marks, sign boards, [[symbols]], [[directions]], signal lights he will be reaching his destination very safely in time. Likewise The [[Buddhist symbols]] are road [[signs]] to reach the abode of [[Enlightenment]]. | ||
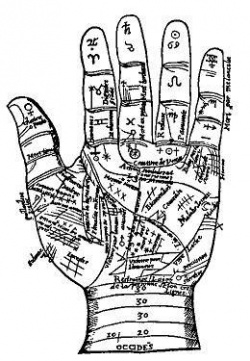
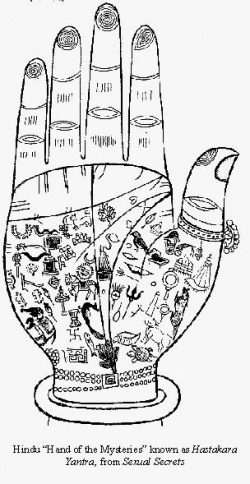
| − | [[Buddhist symbols]] can be categorized into three major divisions A) [[Buddha’s]] personal 32 [[physical]] marks or features representing the [[spiritual]] [[characteristic]] of the [[Buddha]]. B) [[Buddhist]] famous [[Eight symbols]] representing the [[philosophy]] of [[Buddhism]] devised by [[Mahayana Buddhism]] C) [[Buddhist symbols]] or marks or practically {{Wiki|speaking}} figures carved either on the palm of the [[Buddha]] or on the both feet(soles). | + | [[Buddhist symbols]] can be categorized into three major divisions A) [[Buddha’s]] personal 32 [[physical]] marks or features representing the [[spiritual]] [[characteristic]] of the [[Buddha]]. B) [[Buddhist]] famous [[Eight symbols]] representing the [[philosophy]] of |
| + | |||
| + | [[Buddhism]] devised by [[Mahayana Buddhism]] C) [[Buddhist symbols]] or marks or practically {{Wiki|speaking}} figures carved either on the palm of the [[Buddha]] or on the both feet(soles). | ||
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | It should be noted that the [[Buddha’s]] image or statue carved only during the reign of [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] in 2nd C B.C. In the beginning the sculptures took the scales from the ‘[[Lakkhana Sutta]]’ to carve a [[Buddha]] image. It should be further noted that in the beginning the [[Buddha]] image was made in gigantic sizes especially in [[standing]] [[posture]] in rocky hills, not just for [[idolatry]] {{Wiki|purpose}} but to depict him as a [[spiritual guide]] and [[master]] that is too after approximately 400 years of [[Buddha’s]] great demise, [[Mahaparinirvana]]. As such these [[symbols]] can be considered the [[development]] of [[Buddhist]] {{Wiki|architect}} and a method of displaying or [[teaching]] and expounding of [[Buddhism]]. | + | The first category of [[physical]] features of the [[Buddha]] has been mentioned in several [[discourses]] like ‘[[Lakkhana Sutta]]’ in [[Digha Nikaya]] of [[Pali canon]] The First Main [[Division]] ‘[[Sutta Pitaka]]’. So these marks or [[symbols]] or features can be considered as belonging to the [[Buddha’s]] time. The second category of [[symbols]] can be considered belonging to canonization period. The |
| + | |||
| + | third category of [[symbols]] is obviously belonging to post [[canon]] {{Wiki|era}} and also endowed majorly with [[Theravada]] characters. The third group of [[symbols]] or the figures numbering more than 120 have been carved in both palms and soles of the [[Buddha]] and [[108]] [[symbols]] in both soles. Some [[Myanmar]] [[tradition]] is numbering it into 132. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should be noted that the [[Buddha’s]] image or statue carved only during the reign of [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] in 2nd C B.C. In the beginning the sculptures took the scales from the ‘[[Lakkhana Sutta]]’ to carve a [[Buddha]] image. It should be further noted that in the beginning the [[Buddha]] image was made in gigantic sizes especially in [[standing]] [[posture]] in rocky hills, not just for [[idolatry]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Wiki|purpose}} but to depict him as a [[spiritual guide]] and [[master]] that is too after approximately 400 years of [[Buddha’s]] great demise, [[Mahaparinirvana]]. As such these [[symbols]] can be considered the [[development]] of [[Buddhist]] {{Wiki|architect}} and a method of displaying or [[teaching]] and expounding of [[Buddhism]]. | ||
| + | |||
==[[Postures]] And Features Of The [[Buddha]] Image== | ==[[Postures]] And Features Of The [[Buddha]] Image== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 130: | ||
Majorly, [[Buddha]] images are made in three [[postures]] sitting, [[standing]], and reclining.<br/> | Majorly, [[Buddha]] images are made in three [[postures]] sitting, [[standing]], and reclining.<br/> | ||
[[Signs]] of hand position and fingers: (both in sitting and [[standing]] [[postures]]) | [[Signs]] of hand position and fingers: (both in sitting and [[standing]] [[postures]]) | ||
| + | |||
===Sitting [[Postures]]=== | ===Sitting [[Postures]]=== | ||
| + | |||
'''I. The [[Abhaya Mudra]]:''' it is both protecting and [[blessings]] by the [[Buddha]] the focusing of right palm. For protecting the {{Wiki|devotees}} and [[disciples]] the [[Buddha]] always focuses his right palm towards the gatherings. | '''I. The [[Abhaya Mudra]]:''' it is both protecting and [[blessings]] by the [[Buddha]] the focusing of right palm. For protecting the {{Wiki|devotees}} and [[disciples]] the [[Buddha]] always focuses his right palm towards the gatherings. | ||
[[File:Buddha_abhaya_mudra2015.jpg|thumb|centre|250px|This is [[Abhaya mudra]] by right palm]] | [[File:Buddha_abhaya_mudra2015.jpg|thumb|centre|250px|This is [[Abhaya mudra]] by right palm]] | ||
| + | |||
'''II . [[Upadesa Mudra]]''': (Preaching sign - This sign is showed in sitting [[postures]] only) the sign related with [[Sarnath]] and connected with his {{Wiki|sermon}} ‘[[Dhammacakapavathana Sutta]]’. | '''II . [[Upadesa Mudra]]''': (Preaching sign - This sign is showed in sitting [[postures]] only) the sign related with [[Sarnath]] and connected with his {{Wiki|sermon}} ‘[[Dhammacakapavathana Sutta]]’. | ||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
| Line 70: | Line 146: | ||
|[[File:Preaching_mudra_01.jpg|thumb|250px|This is preaching mudra (Saranath posture) ]] || [[File:Preaching_mudra_02.jpg|thumb|250px|This is preaching mudra using both hands (Saranath posture)]] | |[[File:Preaching_mudra_01.jpg|thumb|250px|This is preaching mudra (Saranath posture) ]] || [[File:Preaching_mudra_02.jpg|thumb|250px|This is preaching mudra using both hands (Saranath posture)]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
'''III . [[Bhoomi Sparsa Mudra]]''': (Sitting [[posture]] only) After [[attaining]] of Full [[Enlightenment]], ‘[[Nibbana]]’ as a sign of having conquered the [[evil]] [[Deva]] [[Mara]], The [[Buddha]] touched the [[earth]] with his five fingers of right palm. This shows the great victory as well as [[Full Enlightenment]]. | '''III . [[Bhoomi Sparsa Mudra]]''': (Sitting [[posture]] only) After [[attaining]] of Full [[Enlightenment]], ‘[[Nibbana]]’ as a sign of having conquered the [[evil]] [[Deva]] [[Mara]], The [[Buddha]] touched the [[earth]] with his five fingers of right palm. This shows the great victory as well as [[Full Enlightenment]]. | ||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
| Line 77: | Line 155: | ||
|[[File:Bhoomi_sparsa_mudra_01.jpg|thumb|250px|This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by right hand ([[Buddha Gaya]]) ]] || [[File:Bhoomi_sparsa_mudra_02.jpg|thumb|250px|This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by both hands ( Unusual [[Bhoomi Sparsa mudra]] )]] | |[[File:Bhoomi_sparsa_mudra_01.jpg|thumb|250px|This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by right hand ([[Buddha Gaya]]) ]] || [[File:Bhoomi_sparsa_mudra_02.jpg|thumb|250px|This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by both hands ( Unusual [[Bhoomi Sparsa mudra]] )]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
'''IV . [[Dhyana Mudra]]''' (Sitting [[posture]] only) This [[Mudra]], the [[meditative posture]] which is a common sitting [[posture]] can be seen throughout the [[world]], either carved during 2nd C AD to {{Wiki|modern}} times. It is a sign or [[symbol]] of [[spiritual]] strive as well [[ecstasy]] the [[Buddha]] [[attained]] out of his [[spiritual]] pursuit. This [[posture]] is related with [[Buddhagaya]], where under the [[Bodhi tree]] he strived himself and [[attained]] [[Enlightenment]]. | '''IV . [[Dhyana Mudra]]''' (Sitting [[posture]] only) This [[Mudra]], the [[meditative posture]] which is a common sitting [[posture]] can be seen throughout the [[world]], either carved during 2nd C AD to {{Wiki|modern}} times. It is a sign or [[symbol]] of [[spiritual]] strive as well [[ecstasy]] the [[Buddha]] [[attained]] out of his [[spiritual]] pursuit. This [[posture]] is related with [[Buddhagaya]], where under the [[Bodhi tree]] he strived himself and [[attained]] [[Enlightenment]]. | ||
[[File:Dhyana_mudra_at_Buddha_Gaya.jpg|thumb|centre|250px|This is [[Dhyana mudra]] at [[Buddha Gaya]] ]] | [[File:Dhyana_mudra_at_Buddha_Gaya.jpg|thumb|centre|250px|This is [[Dhyana mudra]] at [[Buddha Gaya]] ]] | ||
| + | |||
===[[Standing]] [[Postures]]=== | ===[[Standing]] [[Postures]]=== | ||
| Line 86: | Line 166: | ||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
|[[File:Standing_abhaya_mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his right palm for protecting and blessings ( [[Abhaya Mudra]]) ]] | |[[File:Standing_abhaya_mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his right palm for protecting and blessings ( [[Abhaya Mudra]]) ]] | ||
|[[File:Left_palm_for_protecting_and_blessings.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his left palm for protecting and blessings (Unusual)]] | |[[File:Left_palm_for_protecting_and_blessings.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his left palm for protecting and blessings (Unusual)]] | ||
| + | |||
|[[File:Both_palms_for_protecting_and_blessings.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his both palms for protecting and blessings (unusual and rare)]] | |[[File:Both_palms_for_protecting_and_blessings.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha uses his both palms for protecting and blessings (unusual and rare)]] | ||
| + | |||
|[[File:Standing_posture_0101.jpg|thumb|250px|Just standing posture (No significance)]] | |[[File:Standing_posture_0101.jpg|thumb|250px|Just standing posture (No significance)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
|[[File:Lotus_and_folding_his_two_elbows_touching_both.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha standing on Lotus and folding his two elbows touching both shoulders. This statue found only one in the world (Pollanaruva, Srilanka)]] | |[[File:Lotus_and_folding_his_two_elbows_touching_both.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha standing on Lotus and folding his two elbows touching both shoulders. This statue found only one in the world (Pollanaruva, Srilanka)]] | ||
|[[File:Buddha_folding_both_elbows_cross_wise_and_touching_his_chest.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha folding both elbows cross wise and touching his chest (Unusual)]] | |[[File:Buddha_folding_both_elbows_cross_wise_and_touching_his_chest.jpg|thumb|250px|In this posture Buddha folding both elbows cross wise and touching his chest (Unusual)]] | ||
| − | |[[File:Buddha_folding_two_palms_as_worshiping.jpg |thumb|250px|This is an unusual image of the Buddha folding two palms as worshiping either God or Gods. According to [[Theravada]] [[tradition]] [[Buddha]] never worshiped by folding two palms. This is against the [[spiritual]] quality of the [[Buddha]] because [[Buddha]] [[attained]] [[Enlightenment]] through his [[own]] [[effort]] not by any [[supernatural]] [[beings]] called [[Devas]], [[Deities]], [[Gods]], [[Goddesses]] etc.,]] | + | |
| + | |[[File:Buddha_folding_two_palms_as_worshiping.jpg |thumb|250px|This is an unusual image of the Buddha folding two palms as worshiping either God or Gods. According to [[Theravada]] [[tradition]] [[Buddha]] never worshiped by folding two palms. This is against the [[spiritual]] [[quality]] of the [[Buddha]] because [[Buddha]] [[attained]] [[Enlightenment]] through his [[own]] [[effort]] not by any [[supernatural]] [[beings]] called [[Devas]], [[Deities]], [[Gods]], [[Goddesses]] etc.,]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
===Reclining [[Posture]]=== | ===Reclining [[Posture]]=== | ||
| + | |||
This reclining [[posture]] has two significances i) first, in a recline [[posture]], if the [[Buddha]] completely rests his head on his entire right hand folded from elbow and the head of the [[Buddha]] rests completely on the right palm, almost both the right palm and head completely resting on the [[earth]] closing both [[eyes]], this [[posture]] shows [[Maha Parinibbana]], the great demise of the [[Buddha]]. | This reclining [[posture]] has two significances i) first, in a recline [[posture]], if the [[Buddha]] completely rests his head on his entire right hand folded from elbow and the head of the [[Buddha]] rests completely on the right palm, almost both the right palm and head completely resting on the [[earth]] closing both [[eyes]], this [[posture]] shows [[Maha Parinibbana]], the great demise of the [[Buddha]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Great_demise_of_the_Buddha.jpg|thumb|250px|This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha ([[Mahaparinibbna]]) ]] | |[[File:Great_demise_of_the_Buddha.jpg|thumb|250px|This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha ([[Mahaparinibbna]]) ]] | ||
|[[File:Great_demise_of_the_Buddha_2.jpg|thumb|250px|This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha ([[Mahaparinibbna]]) ]] | |[[File:Great_demise_of_the_Buddha_2.jpg|thumb|250px|This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha ([[Mahaparinibbna]]) ]] | ||
| Line 108: | Line 198: | ||
If the reclining [[posture]] makes a triangle of left [[alms]] and elbow make an ‘L’ shape and the [[Buddha]] rests his head on the right palm, it shows that the [[Buddha]] either [[meditating]] or relaxing opening of two [[eyes]]. Gigantic [[statues]] have been erected in [[Myanmar]], even 400 feet from head to sole. | If the reclining [[posture]] makes a triangle of left [[alms]] and elbow make an ‘L’ shape and the [[Buddha]] rests his head on the right palm, it shows that the [[Buddha]] either [[meditating]] or relaxing opening of two [[eyes]]. Gigantic [[statues]] have been erected in [[Myanmar]], even 400 feet from head to sole. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | |[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | ||
|[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing3.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | |[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing3.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing2.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | |[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing2.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | ||
|[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing4.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | |[[File:Posture_either_meditating_or_relaxing4.jpg|thumb|250px|Reclining posture either meditating or relaxing]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | '''[[Tibetan]] Finger [[signs]]''':- Technically called ‘[[mudra]]’, which are only the position of fingers of either palm or both the palm at a time. Or keeping the fingers of the both palms in a particular position or pattern for a particular span of time, minimum 20 minutes and to the time of recommended time as [[taught]] by the [[teachers]] which is called ‘[[mudra]]’ practicing. There are only two purposes, generally for [[healing]] only. By keeping the fingers either mixed manner or [[touching]] manner or making a [[form]] through which the functioning of major [[elements]] in the [[physical body]] is set right, especially the proportion of five basic the [[elements]] at par with the [[cosmos]]. (As the paper concerns with only the [[symbols]] carved on the palms and soles of the [[Buddha]], these [[symbols]], [[mudras]], [[signs]], [[postures]] etc.,etc., are not extensively discussed here) | + | |
| + | |||
| + | '''[[Tibetan]] Finger [[signs]]''':- Technically called ‘[[mudra]]’, which are only the position of fingers of either palm or both the palm at a time. Or keeping the fingers of the both palms in a particular position or pattern for a particular span of time, minimum 20 minutes and to the time of recommended time as [[taught]] by the [[teachers]] which is called ‘[[mudra]]’ practicing. There are only two purposes, | ||
| + | |||
| + | generally for [[healing]] only. By keeping the fingers either mixed manner or [[touching]] manner or making a [[form]] through which the functioning of major [[elements]] in the [[physical body]] is set right, especially the proportion of five basic the [[elements]] at par with | ||
| + | |||
| + | the [[cosmos]]. (As the paper concerns with only the [[symbols]] carved on the palms and soles of the [[Buddha]], these [[symbols]], [[mudras]], [[signs]], [[postures]] etc.,etc., are not extensively discussed here) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===Some Examples For The [[Mudras]]=== | ===Some Examples For The [[Mudras]]=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Lotus_mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Lotus mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Lotus_mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Lotus mudra]] ]] | ||
|[[File:Conch Mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Conch Mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Conch Mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Conch Mudra]] ]] | ||
| Line 129: | Line 237: | ||
|[[File:Linga mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Linga mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Linga mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Linga mudra]] ]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Indira’s Lotus mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Indira’s Lotus mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Indira’s Lotus mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Indira’s Lotus mudra]] ]] | ||
|[[File:Cow mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Cow mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Cow mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Cow mudra]] ]] | ||
| Line 134: | Line 244: | ||
|[[File:Maha sacral mudra 2.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Maha sacral mudra]] ( different [[Form]]) ]] | |[[File:Maha sacral mudra 2.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Maha sacral mudra]] ( different [[Form]]) ]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Prana mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Prana mudra]] for receiving [[cosmic]] [[energy]] ]] | |[[File:Prana mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Prana mudra]] for receiving [[cosmic]] [[energy]] ]] | ||
|[[File:Offering mudra .jpg|thumb|250px|[[Offering mudra ]] ]] | |[[File:Offering mudra .jpg|thumb|250px|[[Offering mudra ]] ]] | ||
| Line 145: | Line 259: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|[[File:Meditative mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Meditative mudra]] ]] | |[[File:Meditative mudra.jpg|thumb|250px|[[Meditative mudra]] ]] | ||
| Line 154: | Line 270: | ||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Palm figures showing marks for five elements.jpg|thumb|250px|The palm figures showing marks for five elements]] | |[[File:Palm figures showing marks for five elements.jpg|thumb|250px|The palm figures showing marks for five elements]] | ||
|[[File:Preaching posture.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s right palm in preaching posture ]] | |[[File:Preaching posture.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s right palm in preaching posture ]] | ||
| Line 160: | Line 278: | ||
|[[File:Buddha’s palm with Jewels.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm with Jewels]] | |[[File:Buddha’s palm with Jewels.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm with Jewels]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:Buddha palm carved elephants, drum, conch etc.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm carved with elephants, drum, conch etc.]] | |[[File:Buddha palm carved elephants, drum, conch etc.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm carved with elephants, drum, conch etc.]] | ||
|[[File:Buddha’s palm curved with fish and eye.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm curved with fish and eye of wisdom]] | |[[File:Buddha’s palm curved with fish and eye.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s palm curved with fish and eye of wisdom]] | ||
| Line 167: | Line 287: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The marks or [[symbols]] or figures carved in the soles and palms of the [[Buddha]] represent that the [[Buddha]] is a ‘[[Lokavidu]]’ the knower of entire [[cosmos]] and all [[celestial realms]]. These figures representing {{Wiki|ecology}}, [[animal kingdom]], flora and fauna, birds and {{Wiki|reptiles}} etc., These figures represent not only [[Buddha’s]] [[spiritual]] qualities but also about various [[realms]] like “[[Kama]] [[Loka]]’ the [[worlds]] of [[beings]] having {{Wiki|sensual}} [[faculties]] of [[seeing]], hearing, [[smelling]], [[tasting]], [[touching]] and finally [[thinking]]. The ‘[[Rupa]] [[Loka]]’ [[beings]] having [[forms]] but not {{Wiki|sensual}} {{Wiki|organs}} and finally the [[beings]] in ‘[[Arupa]] [[Loka]]’ the [[realms]] of [[formless]] neither having {{Wiki|sensual}} {{Wiki|organs}} nor [[forms]] but having only the {{Wiki|faculty}} of {{Wiki|conscience}}. | + | The marks or [[symbols]] or figures carved in the soles and palms of the [[Buddha]] represent that the [[Buddha]] is a ‘[[Lokavidu]]’ the knower of entire [[cosmos]] and all [[celestial realms]]. These figures representing {{Wiki|ecology}}, [[animal kingdom]], flora and fauna, birds and {{Wiki|reptiles}} etc., These figures represent not only [[Buddha’s]] [[spiritual]] qualities but also about various [[realms]] |
| + | |||
| + | like “[[Kama]] [[Loka]]’ the [[worlds]] of [[beings]] having {{Wiki|sensual}} [[faculties]] of [[seeing]], hearing, [[smelling]], [[tasting]], [[touching]] and finally [[thinking]]. The ‘[[Rupa]] [[Loka]]’ [[beings]] having [[forms]] but not {{Wiki|sensual}} {{Wiki|organs}} and finally the [[beings]] in ‘[[Arupa]] [[Loka]]’ the [[realms]] of [[formless]] neither having {{Wiki|sensual}} {{Wiki|organs}} nor [[forms]] but having only the {{Wiki|faculty}} of {{Wiki|conscience}}. | ||
===[[Evolution]] Of [[Buddhist Symbols]]=== | ===[[Evolution]] Of [[Buddhist Symbols]]=== | ||
| − | The {{Wiki|concept}} of [[Buddhist symbols]] started from the very first day of the [[Buddha]] emerged in this [[world]] especially marks of his soles, which helped the [[astrologers]] of the [[King]] Suddhothana to predict the {{Wiki|future}} [[life]] of the {{Wiki|prince}} [[Siddhartha]]. After the great demise of the [[Buddha]] ’[[Mahaparinirvana]]’ for remembering the [[teacher]] his {{Wiki|devotees}} inevitably worshiped certain [[forms]]. In the beginning they worshiped ‘[[Bodhi]]’ [[tree]] and later the ’[[Stupas]]’ which are the store houses of the [[Buddha’s]] [[funeral]] ash technically called ‘[[relic]]’. When time passes [[Buddha’s]] personal belongings such as ‘[[alms bowl]]’ ‘saving razor’ and so on. | + | The {{Wiki|concept}} of [[Buddhist symbols]] started from the very first day of the [[Buddha]] emerged in this [[world]] especially marks of his soles, which helped the [[astrologers]] of the [[King]] Suddhothana to predict the {{Wiki|future}} [[life]] of the {{Wiki|prince}} [[Siddhartha]]. After the great demise of the [[Buddha]] ’[[Mahaparinirvana]]’ for remembering the [[teacher]] his {{Wiki|devotees}} |
| + | |||
| + | inevitably worshiped certain [[forms]]. In the beginning they worshiped ‘[[Bodhi]]’ [[tree]] and later the ’[[Stupas]]’ which are the store houses of the [[Buddha’s]] [[funeral]] ash technically called ‘[[relic]]’. When time passes [[Buddha’s]] personal belongings such as ‘[[alms bowl]]’ ‘saving razor’ and so on. | ||
Till the time of [[Asoka]] the great there were only two [[symbols]] “[[Bodhi Tree]]” and “[[stupas]]” erected on the [[relics]] of the [[Buddha]]. Then [[Asoka]] the great built 84000 [[stupas]] in 3rd C. B.C | Till the time of [[Asoka]] the great there were only two [[symbols]] “[[Bodhi Tree]]” and “[[stupas]]” erected on the [[relics]] of the [[Buddha]]. Then [[Asoka]] the great built 84000 [[stupas]] in 3rd C. B.C | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
And the [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] carved gigantic [[Buddha]] images in [[standing]] [[posture]] and due course of time one [[Buddha]] in various [[postures]] came up eventually carving on his palms and soles. | And the [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] carved gigantic [[Buddha]] images in [[standing]] [[posture]] and due course of time one [[Buddha]] in various [[postures]] came up eventually carving on his palms and soles. | ||
According to [[oral tradition]] of [[Burma]] ({{Wiki|modern}} [[Myanmar]]), if a [[practitioner]] of [[Buddha’s]] [[meditative]] system, (either [[Vipassana]] or [[Samatha]]) during [[meditation]] {{Wiki|psychically}} encounters the [[forms]] or figures as found in either sole of the [[Buddha]] or in the palms the [[practitioner]] is [[spiritually]] growing and nearing ‘[[Nibbana]]’ or nearing [[Buddha-hood]]. | According to [[oral tradition]] of [[Burma]] ({{Wiki|modern}} [[Myanmar]]), if a [[practitioner]] of [[Buddha’s]] [[meditative]] system, (either [[Vipassana]] or [[Samatha]]) during [[meditation]] {{Wiki|psychically}} encounters the [[forms]] or figures as found in either sole of the [[Buddha]] or in the palms the [[practitioner]] is [[spiritually]] growing and nearing ‘[[Nibbana]]’ or nearing [[Buddha-hood]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
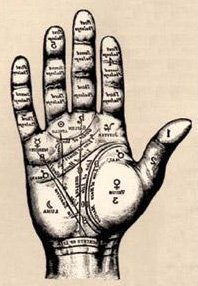
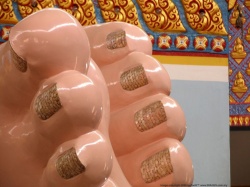
===[[Buddha’s]] Sole Marks Or Prints (Figures)=== | ===[[Buddha’s]] Sole Marks Or Prints (Figures)=== | ||
| − | The {{Wiki|concept}} of [[Buddha’s]] sole print started from the very day of the [[Buddha]]. The [[astrologers]] who examined the [[physical]] features of the new born {{Wiki|prince}} noticed a mark of ‘thousand spokes [[wheel]]’ on his foot and fore-told the [[king]] [[Suddhodana]] the {{Wiki|prince}} would emerge as a Chakravarthi the [[ruler]] of the entire [[earth]]. But among the five members of [[astrologers]] [[Kondanna]] was very firm that the {{Wiki|prince}} would be the ‘[[Guru]]’ for entire [[sentient beings]]. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | The {{Wiki|concept}} of [[Buddha’s]] sole print started from the very day of the [[Buddha]]. The [[astrologers]] who examined the [[physical]] features of the new born {{Wiki|prince}} noticed a mark of ‘thousand spokes [[wheel]]’ on his foot and fore-told the [[king]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Suddhodana]] the {{Wiki|prince}} would emerge as a Chakravarthi the [[ruler]] of the entire [[earth]]. But among the five members of [[astrologers]] [[Kondanna]] was very firm that the {{Wiki|prince}} would be the ‘[[Guru]]’ for entire [[sentient beings]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | {| style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:BuddhaFeet1.jpg|thumb|250px|Only One wheel with one thousand spokes depicting the Buddha as the teacher of all sentient beings.]] | |[[File:BuddhaFeet1.jpg|thumb|250px|Only One wheel with one thousand spokes depicting the Buddha as the teacher of all sentient beings.]] | ||
|[[File:BuddhaFeet2.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s soles endowed with many wheels]] | |[[File:BuddhaFeet2.jpg|thumb|250px|Buddha’s soles endowed with many wheels]] | ||
| Line 189: | Line 325: | ||
|[[File:BuddhaFeet4.jpg|thumb|250px|Foot fingers with Chakras (Wheels)]] | |[[File:BuddhaFeet4.jpg|thumb|250px|Foot fingers with Chakras (Wheels)]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
|[[File:BuddhaFeet5.jpg|thumb|250px|Evolved features, the hoof depicting Tri Ratna]] | |[[File:BuddhaFeet5.jpg|thumb|250px|Evolved features, the hoof depicting Tri Ratna]] | ||
|[[File:BuddhaFeet6.jpg|thumb|250px|The detailed marks and symbols of the soles]] | |[[File:BuddhaFeet6.jpg|thumb|250px|The detailed marks and symbols of the soles]] | ||
| Line 200: | Line 338: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The for the period of 400 years after the great demise of the [[Buddha]], the [[symbols]] were just [[Bodhi Tree]], [[Stupas]] which were built just to store the [[relic]] of the [[Buddha]] and his belongings such as ‘razor’ ‘[[alms bowl]]’ ‘his stitching needle’ etc.,. Only during the reign of [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] the image for the [[Buddha]] was carved on the [[formula]] or the [[physical]] features of the [[Buddha]] as enumerated in the “[[Lakkhana Sutta]]” of [[Pali canon]] [[Digha Nikaya]] of [[sutta]] [[Pitaka]]. In the beginning the [[Buddha]] images were depicted majorly in gigantic [[appearance]] especially [[standing]] and slow by slow sitting [[postures]] and reclining [[postures]] came up. The {{Wiki|concept}} of sole marks or [[symbols]] emerged only from the time of making [[Buddha]] images in reclining [[postures]] exposing his both broad soles. As already explained there are two types of reclining [[postures]], generally resting [[posture]] keeping his on the right palm making a triangle between arm and elbow and resting of his head and this can be also called ‘Reclining [[Meditative]] [[Posture]]’. Another reclining [[posture]] is [[Maha]] Prinibbana, the great demise of the [[Buddha]]. In this [[posture]] the [[Buddha]] totally keeps his entire right hand folding the arm and resting on the ground and the [[Buddha’s]] head is completely kept on the right palm as [[sleeping]]. This [[posture]] denotes the great demise of the [[Buddha]] and not just ‘resting’ or ‘[[meditating]]’. However in the both [[postures]] the both soles of the [[Buddha]] completely exposed and various marks, figures, rightly {{Wiki|speaking}} [[symbols]] are carved. In the [[history of Buddhism]] various [[symbols]] have been evolving to till date. The recent [[symbol]] internationally [[recognized]] is the [[Buddhist flag]] designed by Col.Olcott and others in [[Sri Lanka]]. | + | |
| + | The for the period of 400 years after the great demise of the [[Buddha]], the [[symbols]] were just [[Bodhi Tree]], [[Stupas]] which were built just to store the [[relic]] of the [[Buddha]] and his belongings such as ‘razor’ ‘[[alms bowl]]’ ‘his stitching needle’ etc.,. Only during the reign of [[Emperor]] [[Kanishka]] the image for the [[Buddha]] was carved on the [[formula]] or the [[physical]] features of the [[Buddha]] as enumerated in the “[[Lakkhana Sutta]]” of [[Pali canon]] [[Digha Nikaya]] of [[sutta]] [[Pitaka]]. In the beginning the [[Buddha]] images were depicted majorly in gigantic [[appearance]] especially [[standing]] and slow by slow sitting [[postures]] and | ||
| + | |||
| + | reclining [[postures]] came up. The {{Wiki|concept}} of sole marks or [[symbols]] emerged only from the time of making [[Buddha]] images in reclining [[postures]] exposing his both broad soles. As already explained there are two types of reclining [[postures]], generally resting | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[posture]] keeping his on the right palm making a triangle between arm and elbow and resting of his head and this can be also called ‘Reclining [[Meditative]] [[Posture]]’. Another reclining [[posture]] is [[Maha]] Prinibbana, the great demise of the [[Buddha]]. In this | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[posture]] the [[Buddha]] totally keeps his entire right hand folding the arm and resting on the ground and the [[Buddha’s]] head is completely kept on the right palm as [[sleeping]]. This [[posture]] denotes the great demise of the [[Buddha]] and not just ‘resting’ or | ||
| + | |||
| + | ‘[[meditating]]’. However in the both [[postures]] the both soles of the [[Buddha]] completely exposed and various marks, figures, rightly {{Wiki|speaking}} [[symbols]] are carved. In the [[history of Buddhism]] various [[symbols]] have been evolving to till date. The recent [[symbol]] internationally [[recognized]] is the [[Buddhist flag]] designed by Col.Olcott and others in [[Sri Lanka]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===The [[Evolution]] Of [[Symbols]] Found In [[Buddha’s]] Soles=== | ===The [[Evolution]] Of [[Symbols]] Found In [[Buddha’s]] Soles=== | ||
| − | The {{Wiki|concept}} of sole figures or [[symbols]] started when reclining [[postures]] of the [[Buddha’s]] images were carved. According to [[Myanmar]] [[tradition]] in Sole there are [[108]] [[symbols]] or figures carved. Almost in all images of the [[Buddha]] which are in reclining [[postures]] in the both soles depicting certain marks or [[Buddhist symbols]]. All these figures remind the [[Buddha]] and his [[spiritual]] [[evolution]] from the day of his [[birth]] to [[Maha Parnibbana]] the great demise. Hereunder only the [[spiritual]] aspects of marks or [[symbols]] are extensively discussed | + | |
| + | |||
| + | The {{Wiki|concept}} of sole figures or [[symbols]] started when reclining [[postures]] of the [[Buddha’s]] images were carved. According to [[Myanmar]] [[tradition]] in Sole there are [[108]] [[symbols]] or figures carved. Almost in all images of the [[Buddha]] which are in reclining [[postures]] in the both soles depicting certain marks or [[Buddhist symbols]]. All these figures remind the [[Buddha]] and his | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[spiritual]] [[evolution]] from the day of his [[birth]] to [[Maha Parnibbana]] the great demise. Hereunder only the [[spiritual]] aspects of marks or [[symbols]] are extensively discussed | ||
<poem> | <poem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
I) [[Flowers]] and its varieties: | I) [[Flowers]] and its varieties: | ||
::1.Blue [[Lotus]] | ::1.Blue [[Lotus]] | ||
| Line 213: | Line 368: | ||
::5.Laired [[lotus]] | ::5.Laired [[lotus]] | ||
::6. [[Water]] lily | ::6. [[Water]] lily | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
II) [[Water]] areas: (7-13)Seven Major [[rivers]] of the [[earth]]. (14 -20) Seven big lakes | II) [[Water]] areas: (7-13)Seven Major [[rivers]] of the [[earth]]. (14 -20) Seven big lakes | ||
| + | |||
III) The great Islands: the four great islands and small 2000 islands (21 – 25) | III) The great Islands: the four great islands and small 2000 islands (21 – 25) | ||
| + | |||
IV) The [[Mountains]]: | IV) The [[Mountains]]: | ||
| + | |||
::The seven great [[mountains]] (26 – 32), | ::The seven great [[mountains]] (26 – 32), | ||
::33.Himalayan Mountain | ::33.Himalayan Mountain | ||
::34. [[Maha]] [[Meru]], | ::34. [[Maha]] [[Meru]], | ||
::35. [[Mountains]] of the [[universe]] | ::35. [[Mountains]] of the [[universe]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
V) The ocean 36 | V) The ocean 36 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
VI) The {{Wiki|Planets}}: Planets37, the {{Wiki|sun}} 38, the [[moon]] 39 | VI) The {{Wiki|Planets}}: Planets37, the {{Wiki|sun}} 38, the [[moon]] 39 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
VII) The [[Buddha’s]] {{Wiki|royal}} articles: | VII) The [[Buddha’s]] {{Wiki|royal}} articles: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
::40. Large {{Wiki|spear}} | ::40. Large {{Wiki|spear}} | ||
::41. {{Wiki|royal}} wax [[flower]] | ::41. {{Wiki|royal}} wax [[flower]] | ||
| Line 238: | Line 406: | ||
::53. Pot full of [[water]] | ::53. Pot full of [[water]] | ||
::54. cup full of [[water]] | ::54. cup full of [[water]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
VIII) 55. The sole mark depicting thousand spokes [[wheel]] depicting the [[Buddha]] the [[teacher]] of entire [[cosmos]]. That is he is the [[teacher]] of all [[sentient beings]]. | VIII) 55. The sole mark depicting thousand spokes [[wheel]] depicting the [[Buddha]] the [[teacher]] of entire [[cosmos]]. That is he is the [[teacher]] of all [[sentient beings]]. | ||
IX) 56. Many minor [[wheels]] | IX) 56. Many minor [[wheels]] | ||
X) 57.white [[conch]] shields | X) 57.white [[conch]] shields | ||
XI) 58.pair of [[golden fishes]] | XI) 58.pair of [[golden fishes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
XII) [[Celestial beings]]: | XII) [[Celestial beings]]: | ||
::59. [[Celestial]] Kite [[king]] ([[Garuda]] [[King]]) | ::59. [[Celestial]] Kite [[king]] ([[Garuda]] [[King]]) | ||
| Line 258: | Line 430: | ||
::72. [[Mythical]] {{Wiki|Male}} bird ([[Kinnara]] the [[celestial]] singer) | ::72. [[Mythical]] {{Wiki|Male}} bird ([[Kinnara]] the [[celestial]] singer) | ||
::73. [[Mythical]] {{Wiki|female}} bird ([[Kinnari]] the [[celestial]] singer) | ::73. [[Mythical]] {{Wiki|female}} bird ([[Kinnari]] the [[celestial]] singer) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
XIII) 74 – 79 Six [[Deva realms]] [[celestial abodes]] | XIII) 74 – 79 Six [[Deva realms]] [[celestial abodes]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
XIV) 80 – 96 Sixteen [[Brahmas]]’ [[worlds]] | XIV) 80 – 96 Sixteen [[Brahmas]]’ [[worlds]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
XV) Miscellaneous: | XV) Miscellaneous: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
::97.Palmyra hand fan, | ::97.Palmyra hand fan, | ||
::98.Alms [[bowl]] | ::98.Alms [[bowl]] | ||
| Line 271: | Line 451: | ||
::105-108 - [[Celestial]] Four Doorways | ::105-108 - [[Celestial]] Four Doorways | ||
</poem> | </poem> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
====Commentaries On The Sole Marks and [[Symbols]]==== | ====Commentaries On The Sole Marks and [[Symbols]]==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | In item No I: [[Lotuses]] and other [[flowers]] are shown. From the beginning of the [[Buddha’s]] [[life]] this [[flower]] [[lotus]] does its major role. By his [[own]] words the [[Buddha]] explains “I was delicate, excessively delicate. In my father’s dwelling three [[lotus]] ponds were made purposely for me .Blue [[lotuses]] bloomed in one, red in another, and white in another”.<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Anguttara Nikaya]] Part 1 page 145 (Gradual Sayings)}}</ref> | + | |
| + | As mentioned earlier these marks or figures are substantiating the [[Buddha’s]] [[spiritual]] [[character]] and [[nature]] who could observe the all the [[realms]] and [[abodes]] of the [[cosmos]]. The [[Buddha]] refuted only the [[existence]] of a ‘Creator [[God]]’ but at the same | ||
| + | |||
| + | time approves of presence of many {{Wiki|subtle}} and gross [[worlds]], [[abodes]] and [[realms]] in the [[cosmos]]. As such approving of presence of ‘[[Deities]]’ or ‘[[celestial beings]]’ and even ‘{{Wiki|demons}}’ confined for {{Wiki|punishment}} for one’ [[own]] [[evil deeds]] these are basic [[teachings of the Buddha]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | In item No I: [[Lotuses]] and other [[flowers]] are shown. From the beginning of the [[Buddha’s]] [[life]] this [[flower]] [[lotus]] does its major role. By his [[own]] words the [[Buddha]] explains “I was delicate, excessively delicate. In my father’s dwelling three | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[lotus]] ponds were made purposely for me .Blue [[lotuses]] bloomed in one, [[red]] in another, and white in another”.<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Anguttara Nikaya]] Part 1 page 145 (Gradual Sayings)}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Here the [[Buddha]] talks about a {{Wiki|species}} of plant ‘blue [[lotuses]]’. In {{Wiki|modern}} time this blue variety of [[lotus]] has completely disappeared and [[extinct]]. | Here the [[Buddha]] talks about a {{Wiki|species}} of plant ‘blue [[lotuses]]’. In {{Wiki|modern}} time this blue variety of [[lotus]] has completely disappeared and [[extinct]]. | ||
| + | |||
“Night and day a [[white parasol]] was held over me so that I might not be touched by heat or cold, dust leaves or dew”<ref>{{Nolinking|Ibid, page 128}}</ref> | “Night and day a [[white parasol]] was held over me so that I might not be touched by heat or cold, dust leaves or dew”<ref>{{Nolinking|Ibid, page 128}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
In [[Dhammapada]] [[Buddha]] says that [[lotus]] grows in the mutter [[water]] yet it is not sustained by clay and dust, so as we all born in the [[world]] of [[evils]] and [[sufferings]] but not to be sustained by taint and [[sorrow]]. | In [[Dhammapada]] [[Buddha]] says that [[lotus]] grows in the mutter [[water]] yet it is not sustained by clay and dust, so as we all born in the [[world]] of [[evils]] and [[sufferings]] but not to be sustained by taint and [[sorrow]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The items shown in the number VII: | The items shown in the number VII: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The [[symbols]] such as | The [[symbols]] such as | ||
| Line 292: | Line 491: | ||
:iv)royal cot, | :iv)royal cot, | ||
:v) fan made of pea-cock feather etc., | :v) fan made of pea-cock feather etc., | ||
| + | |||
depicting early luxurious [[life]] style of [[Siddhartha]] and practically {{Wiki|speaking}} imposed on him by his father the [[King Suddhodana]] eventually which made the {{Wiki|prince}} saturated in the [[worldly life]]. The [[Buddha]] asked himself “why do I being [[subject]] to [[birth]], [[decay]], {{Wiki|disease}}, [[death]], [[sorrow]] and [[impurities]], thus search after things of like [[nature]]”.<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Majjhima Nikaya]] Part 1, [[Ariyapariyesana Sutta]] No: 26, p.163}}</ref> | depicting early luxurious [[life]] style of [[Siddhartha]] and practically {{Wiki|speaking}} imposed on him by his father the [[King Suddhodana]] eventually which made the {{Wiki|prince}} saturated in the [[worldly life]]. The [[Buddha]] asked himself “why do I being [[subject]] to [[birth]], [[decay]], {{Wiki|disease}}, [[death]], [[sorrow]] and [[impurities]], thus search after things of like [[nature]]”.<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Majjhima Nikaya]] Part 1, [[Ariyapariyesana Sutta]] No: 26, p.163}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The [[Buddha]] further continues “Cramped and confined is [[household life]], a den of dust, but the [[life]] of [[homeless]] one is as the open [[air]] of [[heaven]]! Hard is it for him who bides at home to live out as it should be lived the [[Holy Life]] in all its [[perfection]], in all its [[purity]].”<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Majjihma Nikaya]] Part 1, [[Mahasaccaka Sutta]], discourse no: 36}}</ref> | The [[Buddha]] further continues “Cramped and confined is [[household life]], a den of dust, but the [[life]] of [[homeless]] one is as the open [[air]] of [[heaven]]! Hard is it for him who bides at home to live out as it should be lived the [[Holy Life]] in all its [[perfection]], in all its [[purity]].”<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Majjihma Nikaya]] Part 1, [[Mahasaccaka Sutta]], discourse no: 36}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The [[symbols]] like Palm-leaf Hand fan, [[alms bowl]] etc., depicting his [[life]] of [[renunciation]]. | The [[symbols]] like Palm-leaf Hand fan, [[alms bowl]] etc., depicting his [[life]] of [[renunciation]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | The items in II to VI: These marks depicting the [[Buddha]] as the knower of entire material [[cosmos]]. According to [[Theravada tradition]] the [[world]] of [[human being]] is called ‘[[Manussa]]’. The [[human realm]] is the mixture of both [[pain]] and [[happiness]]. [[Bodhisatvas]] prefer the [[human realm]] as the best abode to strive to attain [[Buddha-hood]]. As such all the [[Buddha]] are born in [[human realm]]. | + | |
| + | Once on his way to park the first time in his [[life]] his [[karmic]] forces helped him to encounter strange sights of a decrepit old man, a diseased [[person]], a corpse and a dignified [[hermit]]. The first three sights convincingly provided to him, the inexorable [[nature]] of | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[life]], and the [[universal]] ailment of all [[sentient beings]]. The fourth signified the means to overcome the ills of [[life]] and to attain [[calm]] and [[peace]]. The [[Buddha]] declared “[[seeing]] the [[four signs]], I set out on horse-back….”<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Buddhavamsa]] XXVI Page no: 65}}</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The items in II to VI: These marks depicting the [[Buddha]] as the knower of entire material [[cosmos]]. According to [[Theravada tradition]] the [[world]] of [[human being]] is called ‘[[Manussa]]’. The [[human realm]] is the mixture of both [[pain]] and [[happiness]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Bodhisatvas]] prefer the [[human realm]] as the best abode to strive to attain [[Buddha-hood]]. As such all the [[Buddha]] are born in [[human realm]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The items shown in VIII and IX: These [[wheels]] represent [[Buddha’s]] characters that [[Buddha]] is either the {{Wiki|temporal}} sovereign of the [[worlds]] or the [[spiritual master]]. Eventually [[Buddha]] emerged as the [[teacher]] of the [[sentient beings]]. | The items shown in VIII and IX: These [[wheels]] represent [[Buddha’s]] characters that [[Buddha]] is either the {{Wiki|temporal}} sovereign of the [[worlds]] or the [[spiritual master]]. Eventually [[Buddha]] emerged as the [[teacher]] of the [[sentient beings]]. | ||
| + | |||
The items in X and XI are the [[symbols]] of good [[auspicious]] [[signs]], that is ‘[[mangala]]’. There are eight major [[symbols]] in [[Mahayana tradition]]. For example [[mystical]] [[knot]], a [[pair of golden fishes]], [[urn]] and so on. | The items in X and XI are the [[symbols]] of good [[auspicious]] [[signs]], that is ‘[[mangala]]’. There are eight major [[symbols]] in [[Mahayana tradition]]. For example [[mystical]] [[knot]], a [[pair of golden fishes]], [[urn]] and so on. | ||
| + | |||
The items shown in XII depicting that the [[Buddha]] is the knower of all [[celestial]] [[worlds]] ‘[[Lokavidu]]’. By his [[own]] [[word]] the [[Buddha]] says in [[Anguttara Nikaya]] “Not to be reached by going [[worlds]] end” | The items shown in XII depicting that the [[Buddha]] is the knower of all [[celestial]] [[worlds]] ‘[[Lokavidu]]’. By his [[own]] [[word]] the [[Buddha]] says in [[Anguttara Nikaya]] “Not to be reached by going [[worlds]] end” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The item XIII describes about the [[six realms]] of [[Deities]]. The followings are [[six realms]] of ‘[[Devas]]’ or ‘[[Deities]]’ | The item XIII describes about the [[six realms]] of [[Deities]]. The followings are [[six realms]] of ‘[[Devas]]’ or ‘[[Deities]]’ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:i) [[Catummaharajika]] | :i) [[Catummaharajika]] | ||
:ii) [[Tavatmisa]] | :ii) [[Tavatmisa]] | ||
| Line 316: | Line 536: | ||
:v) [[Nimmanarati]] | :v) [[Nimmanarati]] | ||
:vi) [[Paranimmitavasavatti]] | :vi) [[Paranimmitavasavatti]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:1) [[Catummaharajika]]: Very lowest of [[heavenly realms]] where the [[guardian deities]] dwells<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Digha Nikaya]], [[Attanadiya Sutta]]}}</ref>. | :1) [[Catummaharajika]]: Very lowest of [[heavenly realms]] where the [[guardian deities]] dwells<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Digha Nikaya]], [[Attanadiya Sutta]]}}</ref>. | ||
| − | :2) Tavatmisa: Thirty three types of [[deities]] dwells here for this [[realm]] is “The [[King]] [[Indra]]” , but according to [[Theravada tradition]] he is called ‘[[Sakka]]’. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | :2) [[Tavatmisa]]: Thirty three types of [[deities]] dwells here for this [[realm]] is “The [[King]] [[Indra]]” , but according to [[Theravada tradition]] he is called ‘[[Sakka]]’. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:3) [[Yama]]: The [[realm]] of certain higher [[deities]] [[having killed]] the {{Wiki|faculty}} of [[physical]] [[pain]]. | :3) [[Yama]]: The [[realm]] of certain higher [[deities]] [[having killed]] the {{Wiki|faculty}} of [[physical]] [[pain]]. | ||
:4) [[Tusita]]: The [[realm]] of eternal [[happiness]] this may be called as temporary abode for [[Bodhisatvas]] who are to be born as [[future Buddha]]. | :4) [[Tusita]]: The [[realm]] of eternal [[happiness]] this may be called as temporary abode for [[Bodhisatvas]] who are to be born as [[future Buddha]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:5) [[Nimmanarati]]: The [[realm]] of certain [[deities]] who [[delight]] in their created mansions. | :5) [[Nimmanarati]]: The [[realm]] of certain [[deities]] who [[delight]] in their created mansions. | ||
| − | :6) Paranimmitavavatti: The [[realm]] of the [[devas]] who make others’ creation serve their [[own]] ends. These [[Deva worlds]] are temporarily blissful they are too [[subject]] to [[death]] and to be [[reborn]] in some other either higher or lower planes accoding to their ‘[[karmic]] effects’ | + | |
| + | |||
| + | :6) Paranimmitavavatti: The [[realm]] of the [[devas]] who make others’ creation serve their [[own]] ends. These [[Deva worlds]] are temporarily [[blissful]] they are too [[subject]] to [[death]] and to be [[reborn]] in some other either higher or lower planes accoding to their ‘[[karmic]] effects’ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
The item XIV describes about the sixteen [[Brahmas]] [[world]]. {{Wiki|Superior}} to the above mentioned six [[deva realms]] there are sixteen [[worlds of Brahma]]. | The item XIV describes about the sixteen [[Brahmas]] [[world]]. {{Wiki|Superior}} to the above mentioned six [[deva realms]] there are sixteen [[worlds of Brahma]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:1) [[Brama Parisajja]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahma’s]] retinue. | :1) [[Brama Parisajja]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahma’s]] retinue. | ||
:2) [[Brahma Purohita]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahmas]] ministers. | :2) [[Brahma Purohita]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahmas]] ministers. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:3) [[Maha Brahmas]] – The [[realm]] of great [[Brahmas]]. The [[Brahmas]] dwelling in this [[realm]] excel others in [[happiness]], [[beauty]], and age limit owing to [[good deeds]] in their {{Wiki|past}} [[lives]] or [[existences]]. | :3) [[Maha Brahmas]] – The [[realm]] of great [[Brahmas]]. The [[Brahmas]] dwelling in this [[realm]] excel others in [[happiness]], [[beauty]], and age limit owing to [[good deeds]] in their {{Wiki|past}} [[lives]] or [[existences]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:4) [[Paritabha]] – The [[realm]] of Minor Luster. | :4) [[Paritabha]] – The [[realm]] of Minor Luster. | ||
:5) [[Appamanabha]] – The [[realm]] of [[infinite]] Lustre. | :5) [[Appamanabha]] – The [[realm]] of [[infinite]] Lustre. | ||
| Line 336: | Line 574: | ||
:9) [[Subhakinha]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahmas]] of Steady [[Aura]]. | :9) [[Subhakinha]] – The [[realm]] of the [[Brahmas]] of Steady [[Aura]]. | ||
:10) [[Vehapphala]] – The [[realm]] of Great reward. | :10) [[Vehapphala]] – The [[realm]] of Great reward. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:11) [[Asannasatta ]]– The [[realm]] of Mindless [[beings]] but endowed with {{Wiki|conscience}}. | :11) [[Asannasatta ]]– The [[realm]] of Mindless [[beings]] but endowed with {{Wiki|conscience}}. | ||
:12) To 16) [[Suddhavasa]] the [[pure abodes]] with four sub-divisions | :12) To 16) [[Suddhavasa]] the [[pure abodes]] with four sub-divisions | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
::i) [[Aviha]] – The durable [[Realm]], | ::i) [[Aviha]] – The durable [[Realm]], | ||
::ii) [[Atappa]] – [[Serene]] [[Realm]], | ::ii) [[Atappa]] – [[Serene]] [[Realm]], | ||
| Line 343: | Line 585: | ||
::iv) [[Suddassi]] Clear sighted [[realm]] and | ::iv) [[Suddassi]] Clear sighted [[realm]] and | ||
::v) [[Akanittha]] the [[Highest]] [[Realm]]. | ::v) [[Akanittha]] the [[Highest]] [[Realm]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:In item No XV some miscellaneous [[symbols]] are added mixed item of bothe terrestrial as well as [[celestial beings]]. For example {{Wiki|Cow}} and Calf, [[celestial]] pea-cocks, cranes, ruddy {{Wiki|goose}} etc., these items my represents the [[protection]] of the spices. Example [[Asoka]] the great declared many [[animals]] and birds protected in his pillar {{Wiki|edicts}}<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Asoka’s pillar edict]] no:5}}</ref>. | :In item No XV some miscellaneous [[symbols]] are added mixed item of bothe terrestrial as well as [[celestial beings]]. For example {{Wiki|Cow}} and Calf, [[celestial]] pea-cocks, cranes, ruddy {{Wiki|goose}} etc., these items my represents the [[protection]] of the spices. Example [[Asoka]] the great declared many [[animals]] and birds protected in his pillar {{Wiki|edicts}}<ref>{{Nolinking|[[Asoka’s pillar edict]] no:5}}</ref>. | ||
| − | Analysis of [[Symbols]] found in the both soles of the [[Buddha]]: As mentioned earlier the {{Wiki|concept}} of marks or [[symbols]] of soles emerged after making of the [[Buddha]] statue in reclining [[posture]] and it may be either the [[posture]] of great demise or [[relaxation]]. But it should be mentioned that the makers of such [[Buddha]] images did not leave the soles blank. When a [[person]] viewing the reclined [[postures]] of the [[Buddha]] in a [[sense]] of [[devotion]] the marks carved or painted in the soles reminded the [[life of the Buddha]]. For the illiterate populace in those days who cannot either read or write can recollect the [[life of the Buddha]] just [[seeing]] these [[symbols]] or marks carved on the soles. So these [[symbols]] act as telling the [[life]] history of the [[Buddha]] on, the other hand for the higher [[thinking]] [[people]] ‘[[Lokuttara Citta]]’, these marks or [[symbols]] helps to evolve [[spiritually]] and to attain [[Nibbana]] because these marks as already mentioned the [[spiritual]] strive what the [[Buddha]] exercised during his [[spiritual]] quest and also his achievements as the knower of all [[realms]] and the [[teacher]] of all [[sentient beings]] of the [[universe]]. | + | |
| + | |||
| + | Analysis of [[Symbols]] found in the both soles of the [[Buddha]]: As mentioned earlier the {{Wiki|concept}} of marks or [[symbols]] of soles emerged after making of the [[Buddha]] statue in reclining [[posture]] and it may be either the [[posture]] of great demise or [[relaxation]]. But it should be mentioned that the makers of such [[Buddha]] images did not leave the soles blank. When a [[person]] viewing | ||
| + | |||
| + | the reclined [[postures]] of the [[Buddha]] in a [[sense]] of [[devotion]] the marks carved or painted in the soles reminded the [[life of the Buddha]]. For the illiterate populace in those days who cannot either read or write can recollect the [[life of the Buddha]] just | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[seeing]] these [[symbols]] or marks carved on the soles. So these [[symbols]] act as telling the [[life]] history of the [[Buddha]] on, the other hand for the higher [[thinking]] [[people]] ‘[[Lokuttara Citta]]’, these marks or [[symbols]] helps to evolve [[spiritually]] and to | ||
| + | |||
| + | attain [[Nibbana]] because these marks as already mentioned the [[spiritual]] strive what the [[Buddha]] exercised during his [[spiritual]] quest and also his achievements as the knower of all [[realms]] and the [[teacher]] of all [[sentient beings]] of the [[universe]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
{{Centre|BHVATU SABBA MANGALAM<br/> | {{Centre|BHVATU SABBA MANGALAM<br/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Let all beings live in Peace}} | Let all beings live in Peace}} | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Reference [[Books]]== | ==Reference [[Books]]== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Original [[Pali]] and [[Sanskrit]] Texts: | Original [[Pali]] and [[Sanskrit]] Texts: | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:1) [[Digha Nikaya]], [[Sutta Pitaka]] First Main [[Book]] | :1) [[Digha Nikaya]], [[Sutta Pitaka]] First Main [[Book]] | ||
:2) [[Majjhima Nikaya]], [[Sutta Pitaka]] Second main [[Book]] | :2) [[Majjhima Nikaya]], [[Sutta Pitaka]] Second main [[Book]] | ||
:3) [[Anguttara Nikaya]] [[Sutta Pitaka]] Third main [[Book]] | :3) [[Anguttara Nikaya]] [[Sutta Pitaka]] Third main [[Book]] | ||
:4) [[Saddharmapundarika]] | :4) [[Saddharmapundarika]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===Secondary sources=== | ===Secondary sources=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
:1) {{Nolinking|The Hand Book of Tibetan Buddhist Symbols, Serindia Publication Inc. 2003}} | :1) {{Nolinking|The Hand Book of Tibetan Buddhist Symbols, Serindia Publication Inc. 2003}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:26, 5 January 2024
Buddhist Symbols, The Becon Lights To Nibbana
By
Ven. Dr.Bhikkhu Bodhipala
M.A., M.A., M.Phil., D.I.R.D., D.G.Th., Ph.D.,(B.G.L)
Introduction
Symbols
The Forms, figures, drawings, even animal’s heads, marks, color lights, all materials what the humankind uses in his day to day life act as symbols to give a different meaning and conveing a message to the ‘onlookers’ in a particular context and in a particular place. For example a symbol depicting a skull put on two thigh bones warns the seers ‘It is a danger thing
and eventually may leading to death’. An ‘X’ made up of spoon and fork and displayed on the road side indicates the presence of a ‘motel’ or a place of ‘refreshment’.Like this we can give endless examples. Shortly speaking a symbol gives a message it may be a request or a warning or an order and even a spiritual intimation. Letters and numbers also be symbols, because the evolution of
symbols would be a transition from an ideographic to a phonetic scripts which may be or a progress from the linguistic stand point or from the practical use. In ancient Egypt even figures of animals, birds and reptiles stood for
letters. In Chinese language just lines either vertical or horizontal or crosswise or a triangle all stand for conveying the ideas rather than the letters and language. Shortly speaking a form or a figure which stands for an idea becomes a symbol as such a symbol is not mere a form or a picture but perfect manifestation or expression of experience.
Symbols at any rate are the most deep rooted elements of human consciousness. They may be developed into highly aesthetic forms yet their efficacy never depends on their aesthetic values. The success of religions of the
world is due to development of symbols within the particular religion itself out of spiritual gain or experience of its followers. A wooden wheel just having eight spokes is nothing but a representation of entire teachings of the Buddha.
Likewise just two wooden poles put crosswise is the symbol of entire Christianity. A small doll is also a symbol which gives several meanings to a playing child. So symbols are sign of development of human consciousness, in the field of art, literature eventually end in spiritual experience.
 Symbol for eight-fold path |
Type Of Symbols
There are various types of symbols in current usages; THE PATTERN OF SYMBOLS varies according to needs and various fields and disciplines. Like science and technology for example lay out and circuits (in electronic field) do the works of the symbols and in History for example just putting B.C or AD or CE along with numbers gives more information to reckon the years in the field of history.
Chemical Science: In periodic table Roman capital and small letters are marked to denote a type of metal or name of the metal or an element. ‘Au’ stands for gold, likewise ‘Hg’, ‘O’, ‘N’, ‘Nd’, ‘’Na’, ‘H’, ‘Al’, ‘Cl’, and ‘Mg’, all these stand for Mercury, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sodium, Hydrogen, Aluminum, Chlorine and Magnesium respectively.
Letters Standing For Numbers:
In many languages of the world, the ‘scripts or letters’ of the particular language are used as numbers. Capital Roman letters are used as numbers, for example capital ‘I’ stands for number one likewise ‘I’ ‘II’ ‘III’ this sequential values1, 2, and 3 and capital ‘V’ stands for five, if capital ‘I’ is put on the left before capital ‘V’ value ‘one’ is deducted thus it will be the value of 4.
If the capital ‘I’ is put ON THE RIGHT SIDE i.e after ‘V’ the value of 5 is increased, thus ‘V’,’VI’, ‘VII’, ‘VIII’ this sequential makes 5, 6, 7 and 8. Likewise the capital ‘X’ stands for value 10, if as above given method and if capital ‘I’ is put on left side the value ‘one’ is deducted as such it will be the value of 9. And when the capital ‘I’ is put on right side like ‘XI’, ‘XII’, ‘XIII’, the value is increasing
as 11, 12 and 13. The capital ‘L’ stands for the value 40, if capital ‘X’ is put on the right side of capital ‘L’ the value would increase to 50. Shortly speaking in Latin language letters stand for numbers. On the same way the numbers in Tamil Language are only its letters not separate symbols or numbers used. For example the first vowel ‘A’ (Pronounced as ‘and’)
stands for number 8 or value ‘eight’. The first consonant in Tamil ‘Ka’ (pronounced as ‘cut’) stands for the value of ‘one’. Suppose ‘Ka’ and ‘A’ written left right it will be the value of 18 i.e eighteen and the same way ‘A’ and ‘Ka” put left right, it will be the value of 81 i.e eighty one.
Symbols In Mathematics
When a child begins to do sums and calculations knowingly or unknowingly uses many symbols starting from ‘brackets’ ( ) ,‘(+)’ ,‘(-)’, ‘(X)’, ‘(%)’ ,’(<)’, ‘(>)’, ‘(|)’, ‘(\)’, ‘(/)’, ‘(=)’, and so on.
Symbols In Litterary Works
In Literary pieces also the role symbols are inevitable: ‘(,)’, ‘(.)’, ‘(;)’, ‘(:)’, ‘(?)’, ‘(!)’, and they express poetic values and emotions.
Symbols In The Hospitals
In all the hospitals, once we enter into it we come across many sign boards, figures which help everybody to reach or to get one’s requirement.
As explained above symbols’ role is inevitable in all the fields of science. Right from road to home.
Buddhist Symbol
The Buddhist symbols are not concerned with mundane purpose but they aim at spiritual goals and purpose.
A Good driver, if he follows all the road marks, sign boards, symbols, directions, signal lights he will be reaching his destination very safely in time. Likewise The Buddhist symbols are road signs to reach the abode of Enlightenment.
Buddhist symbols can be categorized into three major divisions A) Buddha’s personal 32 physical marks or features representing the spiritual characteristic of the Buddha. B) Buddhist famous Eight symbols representing the philosophy of
Buddhism devised by Mahayana Buddhism C) Buddhist symbols or marks or practically speaking figures carved either on the palm of the Buddha or on the both feet(soles).
The first category of physical features of the Buddha has been mentioned in several discourses like ‘Lakkhana Sutta’ in Digha Nikaya of Pali canon The First Main Division ‘Sutta Pitaka’. So these marks or symbols or features can be considered as belonging to the Buddha’s time. The second category of symbols can be considered belonging to canonization period. The
third category of symbols is obviously belonging to post canon era and also endowed majorly with Theravada characters. The third group of symbols or the figures numbering more than 120 have been carved in both palms and soles of the Buddha and 108 symbols in both soles. Some Myanmar tradition is numbering it into 132.
It should be noted that the Buddha’s image or statue carved only during the reign of Emperor Kanishka in 2nd C B.C. In the beginning the sculptures took the scales from the ‘Lakkhana Sutta’ to carve a Buddha image. It should be further noted that in the beginning the Buddha image was made in gigantic sizes especially in standing posture in rocky hills, not just for idolatry
purpose but to depict him as a spiritual guide and master that is too after approximately 400 years of Buddha’s great demise, Mahaparinirvana. As such these symbols can be considered the development of Buddhist architect and a method of displaying or teaching and expounding of Buddhism.
Postures And Features Of The Buddha Image
Majorly, Buddha images are made in three postures sitting, standing, and reclining.
Signs of hand position and fingers: (both in sitting and standing postures)
Sitting Postures
I. The Abhaya Mudra: it is both protecting and blessings by the Buddha the focusing of right palm. For protecting the devotees and disciples the Buddha always focuses his right palm towards the gatherings.

II . Upadesa Mudra: (Preaching sign - This sign is showed in sitting postures only) the sign related with Sarnath and connected with his sermon ‘Dhammacakapavathana Sutta’.
III . Bhoomi Sparsa Mudra: (Sitting posture only) After attaining of Full Enlightenment, ‘Nibbana’ as a sign of having conquered the evil Deva Mara, The Buddha touched the earth with his five fingers of right palm. This shows the great victory as well as Full Enlightenment.
 This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by right hand (Buddha Gaya) |
 This is Bhoomi sparsa mudra by both hands ( Unusual Bhoomi Sparsa mudra ) |
IV . Dhyana Mudra (Sitting posture only) This Mudra, the meditative posture which is a common sitting posture can be seen throughout the world, either carved during 2nd C AD to modern times. It is a sign or symbol of spiritual strive as well ecstasy the Buddha attained out of his spiritual pursuit. This posture is related with Buddhagaya, where under the Bodhi tree he strived himself and attained Enlightenment.
Standing Postures
 In this posture Buddha uses his right palm for protecting and blessings ( Abhaya Mudra) |
|||
 This is an unusual image of the Buddha folding two palms as worshiping either God or Gods. According to Theravada tradition Buddha never worshiped by folding two palms. This is against the spiritual quality of the Buddha because Buddha attained Enlightenment through his own effort not by any supernatural beings called Devas, Deities, Gods, Goddesses etc., |
Reclining Posture
This reclining posture has two significances i) first, in a recline posture, if the Buddha completely rests his head on his entire right hand folded from elbow and the head of the Buddha rests completely on the right palm, almost both the right palm and head completely resting on the earth closing both eyes, this posture shows Maha Parinibbana, the great demise of the Buddha.
 This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha (Mahaparinibbna) |
 This posture depicting the great demise of the Buddha (Mahaparinibbna) |
If the reclining posture makes a triangle of left alms and elbow make an ‘L’ shape and the Buddha rests his head on the right palm, it shows that the Buddha either meditating or relaxing opening of two eyes. Gigantic statues have been erected in Myanmar, even 400 feet from head to sole.
Tibetan Finger signs:- Technically called ‘mudra’, which are only the position of fingers of either palm or both the palm at a time. Or keeping the fingers of the both palms in a particular position or pattern for a particular span of time, minimum 20 minutes and to the time of recommended time as taught by the teachers which is called ‘mudra’ practicing. There are only two purposes,
generally for healing only. By keeping the fingers either mixed manner or touching manner or making a form through which the functioning of major elements in the physical body is set right, especially the proportion of five basic the elements at par with
the cosmos. (As the paper concerns with only the symbols carved on the palms and soles of the Buddha, these symbols, mudras, signs, postures etc.,etc., are not extensively discussed here)
Some Examples For The Mudras
 Namaskara Mudra (Worshiping or Praying) |
The Symbols, Figures, Forms In The Palm And Soles Of The Buddha
Symbols On The Palm
The marks or symbols or figures carved in the soles and palms of the Buddha represent that the Buddha is a ‘Lokavidu’ the knower of entire cosmos and all celestial realms. These figures representing ecology, animal kingdom, flora and fauna, birds and reptiles etc., These figures represent not only Buddha’s spiritual qualities but also about various realms
like “Kama Loka’ the worlds of beings having sensual faculties of seeing, hearing, smelling, tasting, touching and finally thinking. The ‘Rupa Loka’ beings having forms but not sensual organs and finally the beings in ‘Arupa Loka’ the realms of formless neither having sensual organs nor forms but having only the faculty of conscience.
Evolution Of Buddhist Symbols
The concept of Buddhist symbols started from the very first day of the Buddha emerged in this world especially marks of his soles, which helped the astrologers of the King Suddhothana to predict the future life of the prince Siddhartha. After the great demise of the Buddha ’Mahaparinirvana’ for remembering the teacher his devotees
inevitably worshiped certain forms. In the beginning they worshiped ‘Bodhi’ tree and later the ’Stupas’ which are the store houses of the Buddha’s funeral ash technically called ‘relic’. When time passes Buddha’s personal belongings such as ‘alms bowl’ ‘saving razor’ and so on.
Till the time of Asoka the great there were only two symbols “Bodhi Tree” and “stupas” erected on the relics of the Buddha. Then Asoka the great built 84000 stupas in 3rd C. B.C
And the Emperor Kanishka carved gigantic Buddha images in standing posture and due course of time one Buddha in various postures came up eventually carving on his palms and soles.
According to oral tradition of Burma (modern Myanmar), if a practitioner of Buddha’s meditative system, (either Vipassana or Samatha) during meditation psychically encounters the forms or figures as found in either sole of the Buddha or in the palms the practitioner is spiritually growing and nearing ‘Nibbana’ or nearing Buddha-hood.
Buddha’s Sole Marks Or Prints (Figures)
The concept of Buddha’s sole print started from the very day of the Buddha. The astrologers who examined the physical features of the new born prince noticed a mark of ‘thousand spokes wheel’ on his foot and fore-told the king
Suddhodana the prince would emerge as a Chakravarthi the ruler of the entire earth. But among the five members of astrologers Kondanna was very firm that the prince would be the ‘Guru’ for entire sentient beings.
The for the period of 400 years after the great demise of the Buddha, the symbols were just Bodhi Tree, Stupas which were built just to store the relic of the Buddha and his belongings such as ‘razor’ ‘alms bowl’ ‘his stitching needle’ etc.,. Only during the reign of Emperor Kanishka the image for the Buddha was carved on the formula or the physical features of the Buddha as enumerated in the “Lakkhana Sutta” of Pali canon Digha Nikaya of sutta Pitaka. In the beginning the Buddha images were depicted majorly in gigantic appearance especially standing and slow by slow sitting postures and
reclining postures came up. The concept of sole marks or symbols emerged only from the time of making Buddha images in reclining postures exposing his both broad soles. As already explained there are two types of reclining postures, generally resting
posture keeping his on the right palm making a triangle between arm and elbow and resting of his head and this can be also called ‘Reclining Meditative Posture’. Another reclining posture is Maha Prinibbana, the great demise of the Buddha. In this
posture the Buddha totally keeps his entire right hand folding the arm and resting on the ground and the Buddha’s head is completely kept on the right palm as sleeping. This posture denotes the great demise of the Buddha and not just ‘resting’ or
‘meditating’. However in the both postures the both soles of the Buddha completely exposed and various marks, figures, rightly speaking symbols are carved. In the history of Buddhism various symbols have been evolving to till date. The recent symbol internationally recognized is the Buddhist flag designed by Col.Olcott and others in Sri Lanka.
The Evolution Of Symbols Found In Buddha’s Soles
The concept of sole figures or symbols started when reclining postures of the Buddha’s images were carved. According to Myanmar tradition in Sole there are 108 symbols or figures carved. Almost in all images of the Buddha which are in reclining postures in the both soles depicting certain marks or Buddhist symbols. All these figures remind the Buddha and his
spiritual evolution from the day of his birth to Maha Parnibbana the great demise. Hereunder only the spiritual aspects of marks or symbols are extensively discussed
I) Flowers and its varieties:
1.Blue Lotus
2.red lotus (may be pink)
3.white lotus
4.The garlands of jasmine
5.Laired lotus
6. Water lily
II) Water areas: (7-13)Seven Major rivers of the earth. (14 -20) Seven big lakes
III) The great Islands: the four great islands and small 2000 islands (21 – 25)
IV) The Mountains:
The seven great mountains (26 – 32),
33.Himalayan Mountain
34. Maha Meru,
35. Mountains of the universe
V) The ocean 36
VI) The Planets: Planets37, the sun 38, the moon 39
VII) The Buddha’s royal articles:
40. Large spear
41. royal wax flower
42. Ornament head band
43. Table laid
44. the javelin
45. White parasol
46. The royal scimitar
47. Hand fan made up of pea-cock’s feather
48. The royal whisk made up of antelopes
49. Multi tired roof
50. The arch-way
51. the royal mansion
52. The ruby
53. Pot full of water
54. cup full of water
VIII) 55. The sole mark depicting thousand spokes wheel depicting the Buddha the teacher of entire cosmos. That is he is the teacher of all sentient beings.
IX) 56. Many minor wheels
X) 57.white conch shields
XI) 58.pair of golden fishes
XII) Celestial beings:
59. Celestial Kite king (Garuda King)
60. Crocodile King
61. The Lion king
62. Tiger King
63. Celestial Noble steeds
64. White Elephants
65. Dragon king
66. Golden Swan
67. Golden boats
68. Mount Kailas
69. Celestial Palanquin
70. Noble Bull
71. Indira’s (the king of celestial beings) royal elephants
72. Mythical Male bird (Kinnara the celestial singer)
73. Mythical female bird (Kinnari the celestial singer)
XIII) 74 – 79 Six Deva realms celestial abodes
XIV) 80 – 96 Sixteen Brahmas’ worlds
XV) Miscellaneous:
97.Palmyra hand fan,
98.Alms bowl
99.Celestial Peacock
100. Celestial Crane
101. Cow and her Calf
102. Ruddy Goose
103.Peasent Partridge
104.Golden Leathern
105-108 - Celestial Four Doorways
Commentaries On The Sole Marks and Symbols
As mentioned earlier these marks or figures are substantiating the Buddha’s spiritual character and nature who could observe the all the realms and abodes of the cosmos. The Buddha refuted only the existence of a ‘Creator God’ but at the same
time approves of presence of many subtle and gross worlds, abodes and realms in the cosmos. As such approving of presence of ‘Deities’ or ‘celestial beings’ and even ‘demons’ confined for punishment for one’ own evil deeds these are basic teachings of the Buddha.
In item No I: Lotuses and other flowers are shown. From the beginning of the Buddha’s life this flower lotus does its major role. By his own words the Buddha explains “I was delicate, excessively delicate. In my father’s dwelling three
lotus ponds were made purposely for me .Blue lotuses bloomed in one, red in another, and white in another”.[1]
Here the Buddha talks about a species of plant ‘blue lotuses’. In modern time this blue variety of lotus has completely disappeared and extinct.
“Night and day a white parasol was held over me so that I might not be touched by heat or cold, dust leaves or dew”[2]
In Dhammapada Buddha says that lotus grows in the mutter water yet it is not sustained by clay and dust, so as we all born in the world of evils and sufferings but not to be sustained by taint and sorrow.
The items shown in the number VII:
The symbols such as
- i) large spear,
- ii) Royal mansion,
- iii) ornament head bond
- iv)royal cot,
- v) fan made of pea-cock feather etc.,
depicting early luxurious life style of Siddhartha and practically speaking imposed on him by his father the King Suddhodana eventually which made the prince saturated in the worldly life. The Buddha asked himself “why do I being subject to birth, decay, disease, death, sorrow and impurities, thus search after things of like nature”.[3]
The Buddha further continues “Cramped and confined is household life, a den of dust, but the life of homeless one is as the open air of heaven! Hard is it for him who bides at home to live out as it should be lived the Holy Life in all its perfection, in all its purity.”[4]
The symbols like Palm-leaf Hand fan, alms bowl etc., depicting his life of renunciation.
Once on his way to park the first time in his life his karmic forces helped him to encounter strange sights of a decrepit old man, a diseased person, a corpse and a dignified hermit. The first three sights convincingly provided to him, the inexorable nature of
life, and the universal ailment of all sentient beings. The fourth signified the means to overcome the ills of life and to attain calm and peace. The Buddha declared “seeing the four signs, I set out on horse-back….”[5]
The items in II to VI: These marks depicting the Buddha as the knower of entire material cosmos. According to Theravada tradition the world of human being is called ‘Manussa’. The human realm is the mixture of both pain and happiness.
Bodhisatvas prefer the human realm as the best abode to strive to attain Buddha-hood. As such all the Buddha are born in human realm.
The items shown in VIII and IX: These wheels represent Buddha’s characters that Buddha is either the temporal sovereign of the worlds or the spiritual master. Eventually Buddha emerged as the teacher of the sentient beings.
The items in X and XI are the symbols of good auspicious signs, that is ‘mangala’. There are eight major symbols in Mahayana tradition. For example mystical knot, a pair of golden fishes, urn and so on.
The items shown in XII depicting that the Buddha is the knower of all celestial worlds ‘Lokavidu’. By his own word the Buddha says in Anguttara Nikaya “Not to be reached by going worlds end”
The item XIII describes about the six realms of Deities. The followings are six realms of ‘Devas’ or ‘Deities’
- i) Catummaharajika
- ii) Tavatmisa
- iii) Yama
- iv) Tusita
- v) Nimmanarati
- vi) Paranimmitavasavatti
- 1) Catummaharajika: Very lowest of heavenly realms where the guardian deities dwells[6].
- 2) Tavatmisa: Thirty three types of deities dwells here for this realm is “The King Indra” , but according to Theravada tradition he is called ‘Sakka’.
- 3) Yama: The realm of certain higher deities having killed the faculty of physical pain.
- 4) Tusita: The realm of eternal happiness this may be called as temporary abode for Bodhisatvas who are to be born as future Buddha.
- 5) Nimmanarati: The realm of certain deities who delight in their created mansions.
- 6) Paranimmitavavatti: The realm of the devas who make others’ creation serve their own ends. These Deva worlds are temporarily blissful they are too subject to death and to be reborn in some other either higher or lower planes accoding to their ‘karmic effects’
The item XIV describes about the sixteen Brahmas world. Superior to the above mentioned six deva realms there are sixteen worlds of Brahma.
- 1) Brama Parisajja – The realm of the Brahma’s retinue.
- 2) Brahma Purohita – The realm of the Brahmas ministers.
- 3) Maha Brahmas – The realm of great Brahmas. The Brahmas dwelling in this realm excel others in happiness, beauty, and age limit owing to good deeds in their past lives or existences.
- 4) Paritabha – The realm of Minor Luster.
- 5) Appamanabha – The realm of infinite Lustre.
- 6) Abhassara – The realm of radiant Brahmas.
- 7) Parittanasubha – The realm of Minor Aura.
- 8) Appamanasubha – The realm of the Brahmas of infinite Aura.
- 9) Subhakinha – The realm of the Brahmas of Steady Aura.
- 10) Vehapphala – The realm of Great reward.
- 11) Asannasatta – The realm of Mindless beings but endowed with conscience.
- 12) To 16) Suddhavasa the pure abodes with four sub-divisions
- In item No XV some miscellaneous symbols are added mixed item of bothe terrestrial as well as celestial beings. For example Cow and Calf, celestial pea-cocks, cranes, ruddy goose etc., these items my represents the protection of the spices. Example Asoka the great declared many animals and birds protected in his pillar edicts[7].
Analysis of Symbols found in the both soles of the Buddha: As mentioned earlier the concept of marks or symbols of soles emerged after making of the Buddha statue in reclining posture and it may be either the posture of great demise or relaxation. But it should be mentioned that the makers of such Buddha images did not leave the soles blank. When a person viewing
the reclined postures of the Buddha in a sense of devotion the marks carved or painted in the soles reminded the life of the Buddha. For the illiterate populace in those days who cannot either read or write can recollect the life of the Buddha just
seeing these symbols or marks carved on the soles. So these symbols act as telling the life history of the Buddha on, the other hand for the higher thinking people ‘Lokuttara Citta’, these marks or symbols helps to evolve spiritually and to
attain Nibbana because these marks as already mentioned the spiritual strive what the Buddha exercised during his spiritual quest and also his achievements as the knower of all realms and the teacher of all sentient beings of the universe.
BHVATU SABBA MANGALAM
Let all beings live in Peace
Footnotes
- ↑ Anguttara Nikaya Part 1 page 145 (Gradual Sayings)
- ↑ Ibid, page 128
- ↑ Majjhima Nikaya Part 1, Ariyapariyesana Sutta No: 26, p.163
- ↑ Majjihma Nikaya Part 1, Mahasaccaka Sutta, discourse no: 36
- ↑ Buddhavamsa XXVI Page no: 65
- ↑ Digha Nikaya, Attanadiya Sutta
- ↑ Asoka’s pillar edict no:5
Reference Books
Original Pali and Sanskrit Texts:
- 1) Digha Nikaya, Sutta Pitaka First Main Book
- 2) Majjhima Nikaya, Sutta Pitaka Second main Book
- 3) Anguttara Nikaya Sutta Pitaka Third main Book
- 4) Saddharmapundarika
Secondary sources
- 1) The Hand Book of Tibetan Buddhist Symbols, Serindia Publication Inc. 2003
- 2) Brief History of Symbolism in Buddhism, Web: Exotic India Art
Source
Buddhism And Australia Conference 2015 http://buddhismandaustralia.com/